As data privacy concerns continue to grow in the digital age, businesses globally have had to adapt to new regulations to ensure that their customers’ data is safe and secure. One of the most important of these regulations is the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR), which came into effect in the European Union (EU) on May 25, 2018. The GDPR sets out strict guidelines for using, storing, and collecting personal data, and businesses that do not comply with these guidelines can face significant fines and other penalties.
What is GDPR compliance?
What is the GDPR compliance checklist?
A tool that organizations can use to make sure they are adhering to the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) standards is a GDPR compliance checklist. It typically includes a list of requirements and best practices that organizations should follow to comply with GDPR. A GDPR compliance checklist can help organizations avoid significant fines and other legal consequences associated with non-compliance with GDPR.
GDPR requirements checklist
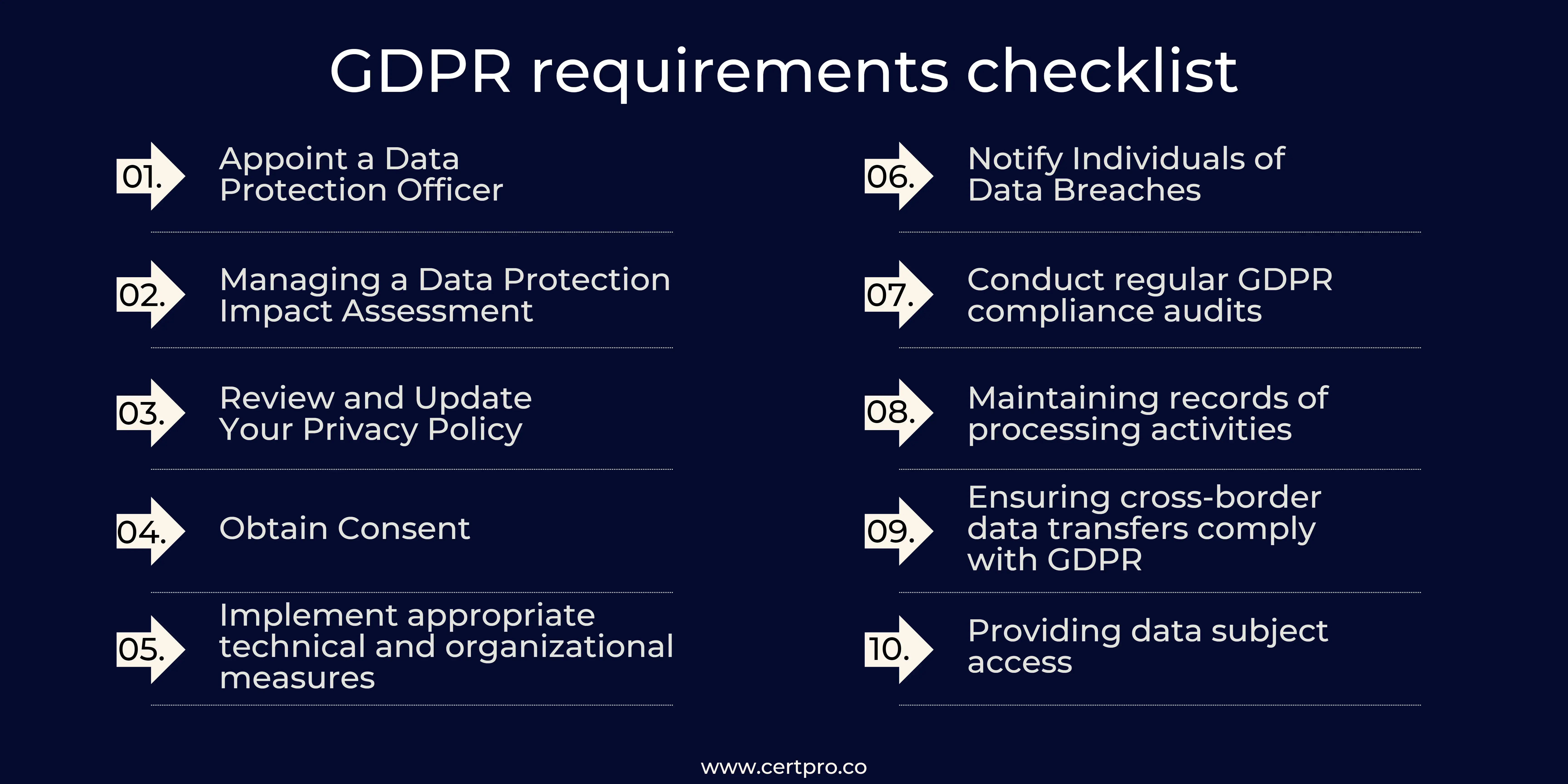
To help businesses ensure that they are compliant with GDPR, we have compiled a GDPR compliance checklist. This checklist covers the main requirements of GDPR and can be used as a template for your business to ensure compliance.
- Appoint a Data Protection Officer (DPO): If your business processes a large amount of personal data, you must designate a Data Protection Officer (DPO) to oversee compliance with GDPR.
- Managing a Data Protection Impact Assessment (DPIA): A DPIA helps you identify and minimize the risks associated with processing data. It is mandatory for specific ways of processing activities, such as those that embrace large-scale processing of sensitive data.
- Review and Update Your Privacy Policy: Your privacy policy should clearly state how you collect, use, and store personal data and how individuals can exercise their rights under GDPR. You should constantly examine and revise your privacy policy to ensure it’s accurate and updated.
- Obtain Consent: Individuals must provide explicit consent for their data to be processed. You should obtain permission from individuals before collecting and using their data and give them the option to withdraw their consent at any time.
- Implement appropriate technical and organizational measures (TOMs): You are required to implement appropriate technical and organizational measures (TOMs) to protect personal data. These include encryption, regular data backups, and security safeguards like access restrictions.
- Notify Individuals of Data Breaches: If your business experiences a data breach that is likely to result in a risk to the rights and freedoms of individuals, you must notify those individuals without undue delay. You should also inform the relevant supervisory authority within 72 hours of becoming aware of the breach.
- Conduct regular GDPR compliance audits: Regular GDPR compliance audits can help you identify areas where you may be lacking in compliance with the GDPR requirements. These audits should include a review of your data processing activities, data protection policies and procedures, and your data breach response plan.
- Maintaining records of processing activities: organizations must maintain detailed records of their data processing activities, including the purposes of the processing, categories of data processed, and data subjects.
- Ensuring cross-border data transfers comply with GDPR: organizations must ensure that any cross-border data transfers comply with GDPR and that appropriate safeguards are in place.
- Providing data subject access: organizations must provide data subjects with information concerning access to their data and request corrections or erasure.
A GDPR compliance checklist can help organizations ensure that they are meeting all the requirements and implementing best practices to protect the personal data of individuals in the EU. By following a GDPR compliance checklist, organizations can avoid significant fines and other legal consequences associated with non-compliance with GDPR. There are also many GDPR compliance checklist templates available online that organizations can use as a starting point for their compliance efforts.
Get expert assistance for GDPR compliance
Finally, complying with the GDPR is essential for organizations that handle the personal data of individuals in the European Union. Failure to comply with GDPR may result in hefty penalties and other legal repercussions. Therefore, using a GDPR compliance checklist can help organizations ensure that they are meeting all the requirements and executing best practices to protect personal data. Certpro, as a consulting company, can assist organizations in obtaining GDPR certification to ensure that they are meeting the highest standards for data protection and privacy. By working with Certpro, organizations can have the confidence and assurance that they are fully compliant with GDPR and other applicable regulations and are taking the necessary steps to protect their customers’ data.
FAQ
Which entities must comply with the GDPR's regulations?
The GDPR (General Data Protection Regulation) applies to any organization that processes the personal data of individuals in the European Union (EU), regardless of where the organization is located. This means that if an organization collects, stores, or processes personal data about EU residents, it must comply with the GDPR. Personal data includes any information that can directly or indirectly identify a person, such as names, addresses, email addresses, IP addresses, and social media profiles. The GDPR applies to all types of organizations, including businesses, non-profits, and government agencies, regardless of their size or industry.
What are the effects of non-compliance with the GDPR?
Non-compliance with the GDPR can result in significant consequences for organizations, including financial penalties, reputational damage, and legal action. The maximum fine for non-compliance is €20 million or 4% of a company’s global annual revenue, whichever is higher. In addition to financial penalties, organizations may also face legal action from individuals whose personal data has been mishandled. Non-compliance can also damage an organization’s reputation and lead to a loss of trust from customers, partners, and other stakeholders. To avoid these consequences, organizations should take GDPR compliance seriously and implement appropriate measures to protect personal data.
What is the GDPR's "right to be forgotten"?
The GDPR’s “right to be forgotten” is a provision that gives individuals the right to request the erasure of their data under certain conditions. This means that individuals can ask organizations to delete their data if it is no longer needed for its original purpose, if the individual withdraws their consent for processing, if the data was obtained unlawfully, or if the data is no longer accurate. The right to be forgotten also requires organizations to take reasonable steps to inform third parties who may have received the data about the erasure request. This provision aims to give individuals greater control over their data and how it is used.
Can an organization transfer personal data outside the EU?
Yes, an organization can transfer personal data outside the European Union (EU) if certain conditions are met. The GDPR (General Data Protection Regulation) requires organizations to ensure that personal data is adequately protected, regardless of where it is transferred. This means that an organization must ensure that the recipient country has adequate data protection laws or that appropriate safeguards are in place, such as standard contractual clauses or binding corporate rules. An organization can also transfer data outside the EU if it obtains the explicit consent of the individual whose data is being transferred. Significant fines and other penalties might be imposed if you fail to comply with these regulations.
How often should an organization review its GDPR compliance program?
An organization should review its GDPR compliance program regularly, and the frequency of these reviews will depend on a range of factors such as the size of the organization, the complexity of its data processing activities, and any changes in relevant laws or regulations. However, it is generally recommended that organizations review their GDPR compliance program at least once a year. This review should assess the effectiveness of the program and identify any gaps or areas for improvement. The review should also take into account any changes in the organization’s data processing activities, such as the introduction of new systems or the collection of new types of personal data.
HOW TO CONDUCT A GDPR AUDIT FOR MY BUSINESS?
The General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) is vital for today's digital landscape. It is a cornerstone for safeguarding people's privacy rights in the European Union (EU). Therefore, organizations dealing with EU residents' data must follow these GDPR rules....
GDPR DATA BREACH NOTIFICATION: THE ULTIMATE GUIDELINE FOR SECURING DATA
Modern businesses require incorporating personal data protection strategies to ensure customer satisfaction and business growth. In this respect, the European Union's General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) sets strict standards for maintaining data security....
GDPR Compliance Software: Boosting Business Efficiency
Handling large amounts of personal data has become a significant concern in today's digital landscape, necessitating a thorough understanding of the intricate legal framework, particularly within the European Union. An essential piece of legislation in this regard is...




