Given the increasing number of cyber threats and assaults, information security is a top issue for businesses of all sizes and industries. An information security management system (ISMS) may help businesses safeguard their information assets and guarantee business continuity. The ISO 27001 standard offers a framework for putting this system into place and keeping it up-to-date. Nearly nine years later, it got a new update to the previous version on October 25, 2022, which is now known as ISO 27001: 2022. Even though there were only a few changes in the new version, it is important to know about them.
The primary distinctions between the two versions of the standard will be discussed in this article, with a focus on the modifications that companies should be aware of when switching to the new version.
ISO 27001: 2022 Revision, What has changed
The new version of the standard includes several significant updates, such as a revised standard title, a major change to Annex A, and some minor modifications to the clauses. The new version of the standard includes several significant updates, such as a revised standard title, a major change to Annex A, and some minor modifications to the clauses. Compared to the 2013 revision, the changes in the 2022 revision of ISO 27001 are generally minimal to moderate. The major section of the standard still consists of 10 clauses, with only minimal revisions made in this section. Similarly, there are only a few changes in the procedures and documentation.
The complete title of the ISO 27001:2022 version, unlike its 2013 predecessor, is ISO/IEC 27001:2022 Information Security, Cybersecurity, and Privacy Protection. The most significant changes in the new version are found in Annex A. The other sections, particularly clauses 4 to 10, only have several minor updates. These include additions to clauses 4.2, 6.2, 6.3, and 8.1, as well as minor changes in sentences, clause restructuring, and terminology. However, the title and order of the clauses remain the same.
Now let’s check out the changes in details made from the previous version to the updated ISO 27001:2022.
Clauses 4 to 10, ISO 27001:2013 vs. ISO 27001:2022
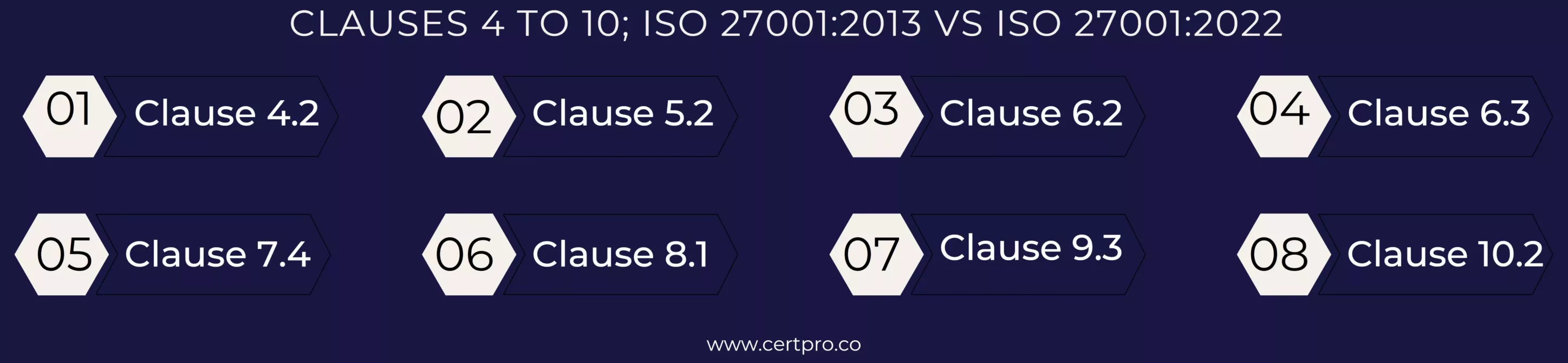
Clause 5.2: Updated Clause 5.2 (leadership) currently sets forth that the top management has to make sure that information security objectives are integrated into the organization’s strategic goals and create an ISMS governance framework.
Clause 6.2: Information security risk assessment Clause 6.2 has been revised to add a need to assess how well current controls are working to manage risks and to take into consideration alternative risk management strategies.
Clause 6.3: Information Security Risk Treatment Clause 6.3, This clause has been revised to include a requirement to prioritize risk treatment alternatives based on the analysis of risk scenarios and to make sure that risk treatment is in line with the organization’s risk management strategy.
Clause 7.4: The modified Clause 7.4 (Communication) stipulates that a method for reporting information security events must be established and kept up-to-date, and that relevant parties must be kept informed of the incidents’ progress and outcome.
Clause 8.1: Clause 8.1 (Operational Planning and Control), This clause has been revised to add the need to design and maintain a procedure for evaluating the effectiveness of information security measures and taking corrective actions as appropriate.
Clause 9.3: An additional subsection was added to Clause 9.3 (Management) Review to make it clear that the organization’s management review must take into account any changes to the demands and expectations of interested parties. Any modifications must be noted since they affect the ISMS‘s scope, which is established in Clause 4 (and based on those needs and expectations). For instance, organizations must take into account how a change in priorities might affect the ISMS if the board of directors of the organization decides to go public.
Clause 10.2: Clause 10.2 (Nonconformity and Corrective Action) has been revised to include a need for determining the most important reason for irregularities and taking steps to correct that major issue in addition to fixing the nonconformity itself.
Changes made to Annex A Control Structure
In comparison to ISO 27001:2013, the control framework has undergone considerable modifications. Here are a few of the significant changes made in ISO 27001:2022:
1. Reorganization of control categories: Information security policies, information security organizations, human resource security, asset management, access control, cryptography, and physical and environmental security are the seven categories into which the control categories have been divided in ISO 27001:2022. This replaces ISO 27001:2013’s previous five categories.
2. Addition of new controls: 16 additional controls have been added to Annex A of ISO 27001:2022 compared to ISO 27001:2013. These new controls include measures for safe development, supply chain security, and data categorization.
3. Removal of some controls: Five controls from Annex A that were in ISO 27001:2013 have been eliminated in ISO 27001:2022. Either these controls were viewed as unnecessary or they were incorporated into other controls.
4. Revision of existing controls: Many of the controls in Annex A have been updated in ISO 27001:2022 to take into account advancements in technology, industry standards, and new threats.
5. Alignment with other standards: Being compatible with other standards In order to be consistent with other ISO management system standards, including ISO 45001 (Occupational Health and Safety Management) and ISO 22301 (Business Continuity Management), ISO 27001:2022 has been amended. Organizations may more easily connect their management systems and cut down on duplication of effort thanks to this alignment.
ISO 27001:2022’s revisions to the Annex A control structure reflects how information security threats and best practices have changed over time and offers a more thorough and organized method of controlling these risks.
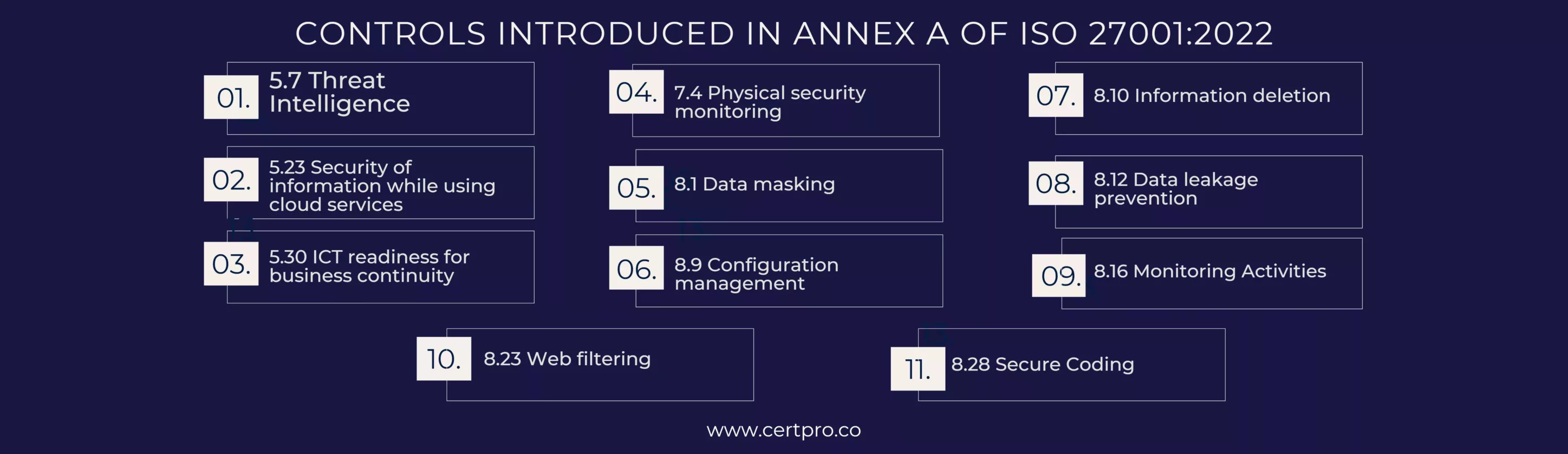
Controls introduced in Annex A of ISO 27001:2022
The modifications to the group listings and the number of controls are included in Annex A of ISO/IEC 27001:2022. The phrase “Reference Control Objectives and Controls” was replaced with “Information Security Controls Reference” in the title. As a result, all control group reference targets from the 2013 edition were eliminated.
From 114 to 93 controls were included in Annex A. As a result of several of them being combined, there was a decrease. While 35 controls stayed the same, 23 were given new names, and one control was split into two; 57 controls were combined into 24 controls. Four control parts now make up the new 93 controls, and they are as follows:
1. 37 new controls were restructured in A.5: Organizational Controls.
2. Eight new controls were restructured in A.6: People Controls.
3. 14 new controls were restructured in A.7: Physical controls
4. 34 new controls were restructured in A.8: Technological controls
In addition, the following 11 additional controls were included in ISO/IEC 27001:2022’s Annex A:
How can CertPro help you get ISO 27001:2022?
From gap analysis through certification, CertPro can offer thorough support at every level of the certification process. Their team of knowledgeable consultants may support you with the creation and implementation of crucial controls and procedures to meet the standard’s requirements, risk assessments, staff training, and internal audits to confirm ongoing compliance.
Overall, working with CertPro will make the ISO 27001:2022 certification process easier and more effective, which will eventually result in successful certification.
FAQ
What is Annex A in ISO 27001?
What new controls have been introduced to Annex A in ISO 27001:2022?
What adjustments were made to the leadership-related information security measures in ISO 27001:2022?
What modifications have been made to ISO 27001 between 2013 and 2022?
Which year had the most revisions to ISO 27001? 2022

About the Author
ANUPAM SAHA
Anupam Saha, an accomplished Audit Team Leader, possesses expertise in implementing and managing standards across diverse domains. Serving as an ISO 27001 Lead Auditor, Anupam spearheads the establishment and optimization of robust information security frameworks.
IS SOC 2 THE SAME AS ISO 27001?
In today's digital landscape, ensuring the safeguarding of client data is paramount for businesses. Adhering to recognized compliance standards is vital to meeting this demand. ISO 27001 vs. SOC 2 represent two prominent benchmarks in the realm of data security with...
WHO NEEDS ISO 27001 CERTIFICATION AND WHY?
The esteemed ISO 27001 security framework is designed to evaluate the effectiveness of an organization's Information Security Management System (ISMS) in safeguarding its data. Obtaining ISO 27001 certification is a practical way for a corporation to demonstrate its...
IS ISO 27001 RISK ASSESSMENT VITAL FOR SECURITY MEASURES?
The ISO 27001 standard provides a framework for information security, highlighting the importance of a thorough risk assessment procedure. Organizations use the methodical and complex ISO 27001 risk assessment process to identify and assess information security...




