Organizations have substantial difficulties defending their priceless information assets from threats and vulnerabilities in today’s connected and data-driven environment. The rise of cyberattacks has highlighted the urgent need to develop effective information security measures. The International Organization for Standardization (ISO) created the ISO 27001 standard to satisfy this demand.
The ISO 27001 implementation framework for Information Security Management System (ISMS) is extensive. The standard includes a number of domains and controls that assist businesses in establishing, maintaining, and advancing their information security processes.
The ISO 27001 domains and controls are explained in this article in a detailed way. We will go into the precise controls that businesses may adopt to safeguard their sensitive information, as well as the many domains that make up the standard. Organizations may manage information security risks, protect their assets, and build stakeholder confidence by complying with the ISO 27001 standard. This article will give you useful insights into the ISO 27001 domains and controls. It doesn’t matter if you’re an information security expert, a corporate executive, or just curious to learn about information security best practices.
WHAT IS ISO 27001:2022?
A company must establish, put into place, maintain, and improve an Information Security Management System (ISMS) in accordance with ISO 27001, an internationally recognized standard. The standard offers a structured method for controlling information security threats and safeguarding sensitive data assets.
The standard focuses on creating a framework of rules, processes, and controls to guarantee the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of information. ISO 27001, which demands that businesses identify and assess information security risks and put in place the necessary controls to reduce them, emphasizes a risk-based approach.
Organizations of all sizes, from all industries and sectors, can use ISO 27001. It offers a widely acknowledged framework for putting best practices in information security into practice.
How does ISO 27001:2022 help companies?
ISO 27001 benefits businesses in a number of significant ways by offering a methodical approach to managing information security risks and developing a strong information security management system (ISMS). Here are some of the significant ways in which this compliance benefits businesses:
- Risk Management: ISO 27001 guides companies in conducting a comprehensive risk assessment to identify and prioritize potential threats and vulnerabilities. By implementing appropriate controls and mitigation strategies, companies can effectively manage and reduce information security risks.
- Legal and Regulatory Compliance: It is essential for firms to stick to all legal, regulatory, and contractual obligations. Companies may better conform their information security procedures to applicable rules and legislation with the aid of ISO 27001.
- Customer Confidence: Information security lapses can negatively affect customer confidence and trust. The ISO 27001 standard for information security management is well-known and widely accepted.
- Internal Process Improvement: The ISO 27001 standard encourages a methodical approach to managing information security. Companies create organized procedures for information handling, access control, incident management, and business continuity planning by putting the requirements of the standard into practice. Internal operations become more effective and efficient as a result, which lowers the risk of security incidents and their related expenses.
- Competitive Advantage: This accreditation may give organizations a marketing advantage. It proves that a company has applied widely acknowledged best practices for information security.
ISO 27001 helps companies establish a solid foundation for managing information security risks, comply with legal and regulatory requirements, build customer trust, improve internal processes, and gain a competitive advantage. It provides a comprehensive framework that enables organizations to proactively protect their valuable information assets and ensure the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of data.
ISO 27001 DOMAINS AND CONTROLS: SAFEGUARDING INFORMATION SECURITY
An information security management system (ISMS) may be created, implemented, maintained, and constantly improved using the guidelines in ISO 27001, an international standard. The standard is split up into many domains that each concentrate on certain facets of information security. Organizations can use particular controls inside each domain to safeguard their information assets. ISO 27001 defines the following domains and controls:
The domains of ISO 27001
The earlier ISO 27001 standard included 11 domains, but the more recent one contains 14. These domains cover six security areas:
- Company security policy
- Asset management
- Physical and environmental security
- Access control
- Incident management
- Regulatory compliance
The 14 domains:
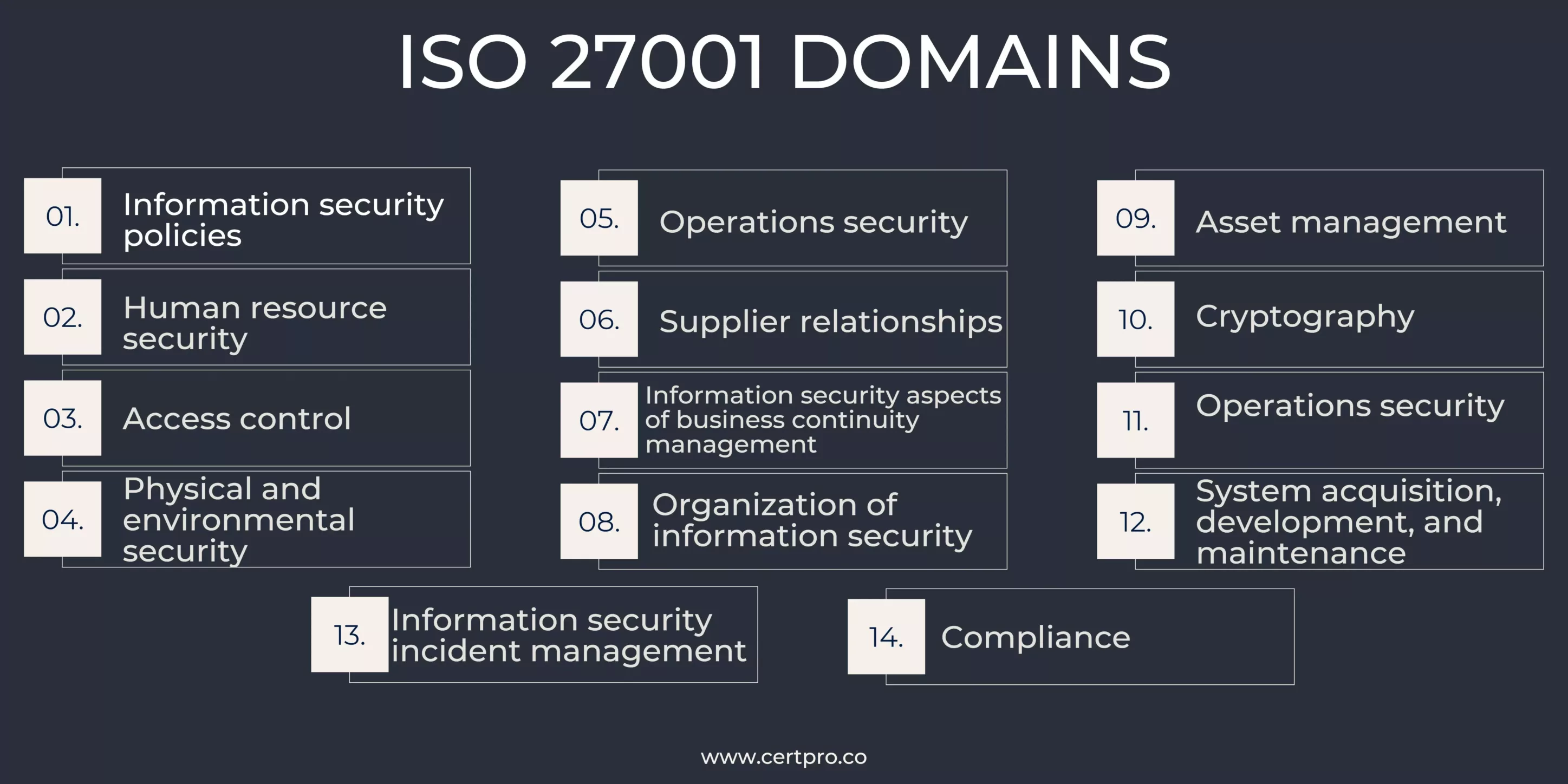
Let’s get to know each domain and the 14 control sets or families within Annex A of ISO 27001, each containing a number of specific controls:
- A.5 Information security policies (2 controls):
This control set has a focus on how information security rules are created, implemented, and maintained inside an organization. By articulating expectations, duties, and rules for safeguarding information assets, it makes sure that there is a clear structure and direction for information security management.
- A.6 Organization of information security (7 controls):
This control set focuses on organizing and structuring information security efforts within an organization. It includes measures to establish roles, responsibilities, and coordination mechanisms to ensure effective implementation and management of information security practices.
It is divided into two sections:
- The organization must have an effective structure in place to adopt and manage information security procedures, and Annex A.6.1 ensures that.
- Annex A.6.2 discusses mobile devices and remote working. Its purpose is to ensure that everyone who works remotely adheres to the proper procedures.
- A.7 Human resource security (6 controls):
This control set addresses security issues relating to employees and staff. It has controls to make sure that workers are aware of their information security obligations, go through the relevant background checks, receive the necessary training, and adhere to the correct processes when hired and fired.
It is divided into three sections:
- Annex A.7.1 focuses on the responsibilities of individuals prior to employment.
- During employment, Annex A.7.2 encompasses their responsibilities.
- Once individuals have left the organization or changed positions, Annex A.7.3 outlines their responsibilities.
- A.8 Asset Management (10 controls):
The management of information assets is the subject of this control set. It contains controls for categorizing information, implementing suitable security measures depending on asset value and sensitivity, identifying and inventorying information assets, establishing ownership, ensuring permissible usage, and ensuring acceptable use.
It has three sections:
- Organizations’ identification of information assets that fall under the purview of the ISMS is the main topic of Annex A.8.1.
- The Classification of information is covered in Annex A.8.2. By following this procedure, information assets are guaranteed to receive the proper level of protection.
- In accordance with Annex A.8.3, media handling must prevent the unauthorized disclosure, alteration, removal, or destruction of sensitive data.
- A.9 Access control (14 controls):
Access control is essential for preventing illegal access to information. This control set offers safeguards to guarantee that access to data and systems is restricted to those who are permitted and is based on clearly defined roles, responsibilities, and business requirements.
It is broken down into four components that cover:
- A.9.1 business need for access controls
- A.9.2 managing user access
- A.9.3 user responsibilities
- A.9.4 controlling access to systems and applications
- A.10 Cryptography (2 controls):
Through encryption and other cryptographic methods, cryptography controls aim to safeguard the confidentiality, integrity, and validity of information. When sensitive data is being stored, transmitted, or processed, these measures help protect it.
It is divided into two parts:
- A.10.1 Cryptographic controls
- A.10.2 Cryptographic key management
- A.11 Physical and Environmental Security (15 controls):
Physical security measures focus on safeguarding tangible resources, buildings, and assets. They include steps like equipment protection, clear desk and screen regulations, access restrictions to secure locations, and proper asset disposal to avoid unwanted access or damage.
The 15 controls are divided into two parts:
- A.11.1 protects the sensitive data from threats, unauthorized access, and interference.
- Annex A.11.2 focuses exclusively on equipment. It is intended to stop the theft, loss, or damage of containers holding information assets for an organization.
- A.12 Operation controls (14 controls):
This control set encompasses the operational facets of information security. It has controls for establishing and putting into practice operating processes, guarding against malware, performing routine backups, and making sure that security incidents are properly monitored and recorded.
These 14 controls got fitted in 7 sections:
- Annex A.12.1 of ISO 27001 focuses on operational procedures and responsibilities to ensure the establishment of proper operational practices within an organization.
- In Annex A.12.2, the standard addresses the topic of malware and emphasizes the need for organizations to have robust defenses in place to mitigate the risk of infection.
- Annex A.12.3 pertains to the requirements for system backup, aiming to prevent data loss by outlining guidelines for regular and effective backup processes.
- The purpose of Annex A.12.4 is to highlight the importance of logging and monitoring within an organization. This section ensures that organizations maintain documented evidence of security events, facilitating effective incident response and detection.
- In Annex A.12.5, the focus is on safeguarding the integrity of operational software. This section outlines measures to protect against unauthorized modifications or tampering with software used in operational processes.
- Annex A.12.6 addresses technical vulnerability management, ensuring that organizations actively identify and address system weaknesses to prevent exploitation by unauthorized parties.
- Lastly, Annex A.12.7 addresses information systems and audit considerations. Its goal is to reduce the disruption that audit activities cause on operational systems, allowing for a seamless integration of auditing processes while maintaining system functionality.
- A.13 Communication security (7 controls):
Communication security measures are in place to protect the sharing and transmission of information. They include steps to safeguard network infrastructure, protect data while it is being transmitted, guarantee secure electronic commerce, and keep an eye on communication channels for possible security holes.
It’s divided into two sections:
- Network security management is addressed in Annex A.13.1 in order to maintain the confidentiality, integrity, and accessibility of information in such networks.
- Security is addressed in Annex A.13.2 when providing information to clients or other interested parties, whether inside or outside the organization.
- A.14 System acquisition, development, and maintenance (13 controls):
This collection of controls addresses security issues that arise during an information system’s lifespan. Defining security requirements, developing and testing secure systems, and guaranteeing the safe administration of system modifications and upgrades are among its components.
- A.15 Supplier relationships (5 controls):
The management of information security risks connected with third-party suppliers is the main goal of these measures. In order to ensure compliance with security standards, they also construct contractual agreements, monitor supplier performance, and analyze and manage supplier security.
There are two sections:
- The protection of an organization’s priceless assets that are accessible to or impacted by suppliers is covered in Annex A.15.1 of the regulations.
- Annex A.15.2 is designed to ensure that both parties maintain the agreed level of information security and service delivery.
- A.16 Information security incident management (7 controls):
The controls in this set deal with the management of information security occurrences and incidents. They include procedures for documenting and responding to occurrences, figuring out their effects, stopping them altogether, and making adjustments to stop them from happening again.
- A.17 Business Continuity Management Information Security Aspects (4 controls)
This control set covers the incorporation of information security into business continuity management procedures. In addition to developing redundancy and testing and maintaining business continuity plans, it also includes steps for identifying and addressing information security continuity threats.
Also, this got divided into two parts:
- Annex A.17.1 describes the steps that may be taken to guarantee that information security continuity is integrated into the business continuity management system of the organization.
- Redundancies are examined in Annex A.17.2 to ensure the availability of information processing facilities.
- A.18 Compliance (8 controls):
Compliance controls are aimed at ensuring that the business complies with contractual, legal, and regulatory obligations regarding information security. They consist of procedures for carrying out compliance audits, evaluating technical compliance, and resolving any non-compliance concerns found.
IDENTIFY THE CONTROLS YOU NEED TO IMPLEMENT
Organizations do not have to implement every one of the 114 measures listed in ISO 27001. The standard includes a detailed list of ISO 27001:2022 Domains & Controls as a guide, but the choice and application of controls should be based on an evaluation of the risks and the unique requirements of the business.
ISO 27001 encourages organizations to assess their information security risks and select the most effective policies to effectively reduce such risks. The process of risk assessment aids in determining the most significant weaknesses, threats, and possible effects on information assets. Organizations can prioritize and choose controls that are pertinent and essential for their unique environment based on the findings of the risk assessment.
Establishing an information security management system (ISMS) that is customized to the needs of the enterprise is the goal of ISO 27001 certification. The ability to apply controls that are suitable and proportionate to their risk profile, size, complexity, and industrial sector is what this means for businesses.
CERTPRO: THE LEADING ISO 27001:2022 AUDITOR
Enterprises can develop and maintain effective information security management systems thanks to the comprehensive framework that ISO 27001 offers. Despite the fact that the standard lists 114 measures, companies are free to choose and apply certain controls depending on their unique risks and requirements.
Certification to ISO 27001 demonstrates an organization’s commitment to information security and adherence to generally accepted best practices. Organizations may reduce security risks, safeguard sensitive information, and maintain regulatory compliance by putting the right controls in place that were discovered during risk assessment.
Organizations may receive help from CertPro, a reputable certification company, to become ISO 27001 certified. Their knowledge of ISO 27001 standards compliance and information security management systems may help firms install controls, conduct risk assessments, and achieve certification.
FAQ
Are all 114 controls really necessary for organizations to implement?
The 114 controls are not all mandated for implementation by organizations. A risk assessment and the particular security requirements of the company should be taken into consideration when choosing and implementing measures.
What is the first step in putting ISO 27001 into practice?
-
As part of the ISO 27001 implementation process, the organization must carry out a risk assessment to identify and evaluate information security threats specific to the organization. This evaluation determines the measures that the organization must put in place to effectively reduce those risks.
Does ISO 27001 require continuous maintenance or is it a one-time certification?
Maintaining ISO 27001 certification is necessary. To keep their certification, organizations must regularly audit and evaluate their information security management system, continuously monitor and enhance it, and resolve any risks or non-conformities that are found.
How many new controls does ISO 27001 include?
On February 15, 2022, ISO 27002:2022 (Controls for information security, cybersecurity, and privacy protection) was published. Since then, ISO 27001:2022 has synchronized its Annex A controls. A streamlined set of 93 Annex A controls, including 11 new controls, is used in the revised edition of the Standard.
How many different categories does ISO 27001 have?
Organizations must have controls in place that adhere to ISO 27001’s requirements for an information security management system. Annex A, which lists all ISO 27001 controls and divides them into 14 categories is part of the ISO 27001 standard specification.

About the Author
ANUPAM SAHA
Anupam Saha, an accomplished Audit Team Leader, possesses expertise in implementing and managing standards across diverse domains. Serving as an ISO 27001 Lead Auditor, Anupam spearheads the establishment and optimization of robust information security frameworks.
IS SOC 2 THE SAME AS ISO 27001?
In today's digital landscape, ensuring the safeguarding of client data is paramount for businesses. Adhering to recognized compliance standards is vital to meeting this demand. ISO 27001 vs. SOC 2 represent two prominent benchmarks in the realm of data security with...
WHO NEEDS ISO 27001 CERTIFICATION AND WHY?
The esteemed ISO 27001 security framework is designed to evaluate the effectiveness of an organization's Information Security Management System (ISMS) in safeguarding its data. Obtaining ISO 27001 certification is a practical way for a corporation to demonstrate its...
IS ISO 27001 RISK ASSESSMENT VITAL FOR SECURITY MEASURES?
The ISO 27001 standard provides a framework for information security, highlighting the importance of a thorough risk assessment procedure. Organizations use the methodical and complex ISO 27001 risk assessment process to identify and assess information security...




