The need to safeguard people’s privacy is more important than ever in the modern digital environment, where personal data has turned into a valuable asset. It has become crucial to implement strong protections and give people control over their own data in light of the development of new technologies and the ubiquitous collection and processing of personal data.
The European Union (EU) adopted the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) in 2018, which established a broad range of rights aimed at safeguarding people’s privacy and ensuring ethical data handling practices by enterprises. In addition to giving people more control over how their data is used, the GDPR’s eight individual rights also create a framework for openness, responsibility, and moral data processing.
In this article, we will explore each of these rights and delve into their significance in safeguarding privacy and promoting a user-centric approach to data protection. To help you understand each of the eight fundamental rights, we’ve listed them below with a brief description.
THE PRIMARY GOAL OF GDPR
The main purpose of the GDPR is that, whether a company is based inside the EU or outside of it but provides products or services to EU residents, it applies to all businesses that manage the private data of EU citizens. Giving people more control over their personal data and requiring corporations to treat it responsibly and securely are the two main objectives of GDPR.
The rights outlined in the GDPR were created to give people more control over their personal data and to promote data protection and privacy for EU residents. When drafting the GDPR, the EU took into account a number of legal and privacy frameworks as well as suggestions from stakeholders, privacy experts, and data protection agencies. The objective was to create a thorough and uniform set of laws and rights for data protection across EU members. The GDPR took its place on May 25, 2018, in place of the Data Protection Directive from 1995.
The EU created the GDPR, but its effects go beyond its borders. No matter if a company is based inside the EU or outside of it but provides products or services to EU residents, it must comply if it handles personal data of EU persons. Individuals have the ability to actively assert the rights afforded by the GDPR with the companies that handle their personal data.
HOW TO ACHIEVE GDPR?
Achieving GDPR compliance requires a systematic approach and a commitment to protecting individuals’ privacy rights. You can get started by following these steps:
1. Understand the Requirements: Familiarize yourself with the provisions and principles of the GDPR. Ensure you have a clear understanding of how it applies to your organization, the types of data you collect, and the processing activities you undertake.
2. Perform a data audit: Carefully examine the personal information you gather, keep, and use. Identify the processing’s legal justification, objectives, duration of data retention, and any associated third parties.
3. Update Privacy Policies and Notices: Revision and updating of privacy policies and notifications is necessary to comply with GDPR regulations. Make sure they are easily available, written in clear and simple language, and notify people about their rights, how their data is processed, and how to exercise their rights.
4. Obtain the legal justification for processing: Determine and record the legal justification for processing personal data. Consent, contract performance, legal requirements, legitimate interests, and essential interests are examples of common basis. Make sure you have authorized, written consent where it is needed.
5. Establish Data Subject Rights Processes: To manage requests for access, correction, deletion, limitation of processing, data portability, and objection, it is necessary to establish data subject rights processes. Create a method for confirming people’s identities and react to inquiries within the allotted time.
6. Implement data security measures: Put suitable technological and organizational safeguards in place to protect the security of personal data by implementing data security procedures. This includes encryption, access limits, frequent backups, staff education on data safety, and protocols for handling data breaches in the event of an incident.
7. Conducting Data Protection Impact Assessments (DPIAs): Performing Data Protection Impact Assessments DPIAs should be conducted for high-risk processing operations that pose a significant danger to the rights and freedoms of individuals. Determine if the processing is necessary and appropriate, identify any hazards, and put precautionary measures in place.
8. Examine Data Transfers: Before transferring personal information outside of the European Economic Area (EEA), make sure that the necessary protections are in place, such as Standard Contractual Clauses (SCCs), Binding Corporate Rules (BCRs), or certification processes.
9. Partner and Vendor Management: Ensure that contracts with third-party contractors are reviewed and updated to reflect the GDPR’s standards for data protection. Do your research about their data protection procedures.
10. Staff Training and Education: Regularly teach staff members about GDPR standards, best practices for data protection, and their roles and responsibilities in protecting personal data.
11. Monitor and assess compliance: To maintain continuous compliance with the GDPR, you should routinely monitor and assess your data processing operations, privacy policies, and security precautions. If required, conduct internal audits or hire outside consultants.
12. Appoint a Data Protection Officer (DPO): If necessary, name a DPO who will be in charge of ensuring that your company complies with GDPR and functions as a point of contact for clients and regulatory agencies.

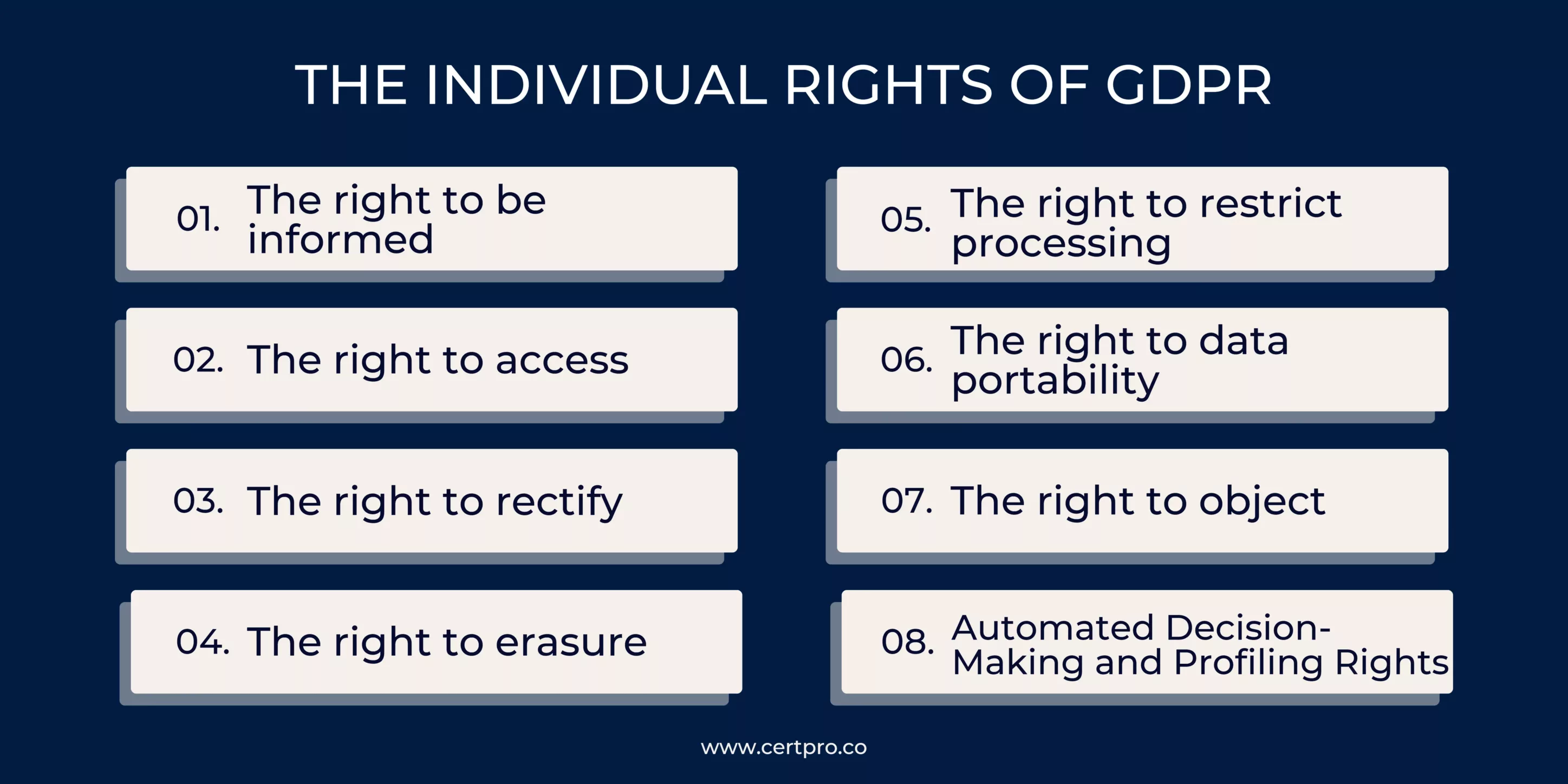
THE INDIVIDUAL RIGHTS OF GDPR
The eight rights outlined in the GDPR are essential for enterprises to adhere to for a number of reasons. First of all, the GDPR is a legal framework with which businesses that process personal data of EU citizens must comply. Protecting people’s privacy requires upholding the rights specified in the GDPR. Organizations may show they respect people’s privacy and autonomy by upholding these rights and ensuring that their personal data is handled carefully and responsibly.
Following the eight rights that individuals have under the General Data Protection Regulation is crucial for a number of reasons. They are:
The right to be informed: One of the fundamental rights guaranteed to people by the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) is the right to information, commonly known as the right to be informed. This right gives people the ability to obtain clear and transparent information about how businesses acquire, handle, and utilize their personal data.
Establishing trust and empowering people to make knowledgeable decisions regarding the processing of their personal data depend on their right to information. Organizations are required to give people certain information when they gather personal data, such as:
- Identity of the Data Controller
- Authority on their personal data
- Legal Justification
- Data Retention Period
- Access for personal data
- Data Transfers
The right to access: Individuals’ right of access enables them to learn about and confirm the legitimacy and fairness of the processing of their personal data. People are better equipped to exert more control over their personal information when they are aware of how and why it is being utilized.
Here are the key aspects of the right to access:
- Confirmation of data processing
- Access to personal data
- Providing copies of data
- Process for requesting access
- Reasonable fees and timeframes
The right to rectify: By exercising their right to rectification, people may make sure that the personal information that organizations hold on them is true and current. It gives people the capacity to regulate their personal information and ward off any harm or unfavorable effects that can result from using inaccurate or out-of-date information.
The key aspects of the right to rectify are:
- updating info that is incorrect or lacking
- Additional statement
- Notification of outsiders
- Procedure for making a correction request
- Duration of the correction
The right to erasure: Individuals can manage the retention and use of their personal data by exercising their right to erasure. It acknowledges the value of privacy and allows people to ask for the deletion of their personal data when it is no longer required, when permission is withdrawn, when the processing is unlawful, or when there are other justifiable grounds for it.
The key aspects of the right to erasure are:
- Request for data deletion
- Obligation for data controllers
- Communication to third parties
- Retention periods and legal obligations
- Exceptions to the right of erasure
The right to restrict processing: Individuals have control over how their personal data is used while unresolved problems or disputes are being handled thanks to the right to prohibit processing. It enables people to restrict or temporarily stop the processing of their data without necessarily asking for its erasure.
A few key aspects of the right to restrict processing are:
- Request for restriction
- Grounds for restriction
- Temporary limitation
- Communication of restriction
- Data retention during restriction
- Notification of lifting the restriction
The right to data portability: People who have the right to data portability are able to request and receive their personal information from a company in a structured, widely used, and machine-readable format. When technically possible, this format makes it simple to transfer the data to another organization, either directly between organizations or by an individual.
Key aspects of data portability are:
- Request for data portability
- Scope of data portability
- Transfer formats
- Direct transfer option
- Timeframe for data portability
- Limitations to data portability
The right to object: The right to object enables people to voice their disapproval and ask that a company cease processing their personal data. The purpose of this right is to offer people more control over their data and guarantee that their interests and basic rights are upheld.
A few important aspects of the right to object:
- Grounds for objection
- Direct marketing
- Profiling
- Process for objecting
- Assessing the objection
- Notifying individuals
Automated Decision-Making and Profiling Rights: The General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) contains special rights pertaining to profiling and automated decision-making. These rights are meant to safeguard people against potentially negative outcomes brought on by choices that are entirely based on automated processing without human involvement.
Here are the key aspects of the rights related to automated decision-making and profiling:
- Right to information:
- Right to explanation
- Right to object
- Human review
- Safeguards for children
- Legal limitations and exceptions
The eight rights that people have under GDPR are crucial for maintaining privacy, control, and responsibility in the digital sphere. The GDPR gives people more control over their personal information by allowing them to view, update, delete, and restrict how their data is processed. Additional protections are offered through the rights to data portability, opposition, and automated decision-making, which also support openness and justice. Organizations may develop trust, promote a culture of privacy, and show their dedication to safeguarding personal data by enforcing and upholding these rights. The significance of these rights cannot be overemphasized as we traverse the constantly changing digital world because they lay the groundwork for a more user-centric and privacy-conscious data economy.
How does CERTPRO assist you in meeting GDPR compliance?
Organizations may benefit from CertPro’s experience and direction in a number of crucial areas. We help with data audits, updating privacy notifications and policies, and setting up procedures for dealing with requests for data subject rights. In order to secure compliance across the whole data ecosystem, CertPro can also offer helpful insights into putting data security measures into place, conducting data protection impact assessments, and managing vendor relationships.
Organizations may benefit from the expertise and experience in GDPR compliance that a reputable service provider like CertPro can provide. Organizations may improve their data security procedures, expedite their compliance operations, and show a commitment to preserving people’s rights to privacy by utilizing their knowledge.
FAQ
Why is GDPR so important?
The GDPR is significant because it reinforces people’s rights and gives them more power over their personal data. Additionally, it places requirements on organizations to ensure the legal and open handling of data, which promotes confidence between customers and companies.
Is GDPR compliance a one-time effort?
The process of GDPR compliance is continuing. Organizations must continuously examine and analyze their data processing operations, alter their procedures as needed, and keep up with legislative changes. It is important to undertake regular audits and assessments to guarantee continuing compliance and flexibility in response to changing data privacy standards.
Can businesses comply with the GDPR without outside help?
Yes, firms can comply with GDPR without outside help, but it can be harder and take longer. Service providers with extensive experience, such as CertPro, may facilitate compliance, guarantee complete compliance with GDPR rules, and offer insights into best practices for data security.
What are the consequences of GDPR non-compliance?
Non-compliance with GDPR can result in imposing significant fines, which can reach up to €20 million or 4% of the organization’s global annual revenue, whichever is bigger. In addition, businesses may face brand harm, a decline in consumer confidence, and the potential for legal action from individuals harmed by data breaches or privacy violations.
Who is exempt from the GDPR?
The UK GDPR does not apply to certain actions, including those that fall under the Law Enforcement Directive, those required to maintain national security, and those carried out solely for domestic or personal use.

About the Author
RAGHURAM S
Raghuram S, Regional Manager in the United Kingdom, is a technical consulting expert with a focus on compliance and auditing. His profound understanding of technical landscapes contributes to innovative solutions that meet international standards.
HOW TO CONDUCT A GDPR AUDIT FOR MY BUSINESS?
The General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) is vital for today's digital landscape. It is a cornerstone for safeguarding people's privacy rights in the European Union (EU). Therefore, organizations dealing with EU residents' data must follow these GDPR rules....
GDPR DATA BREACH NOTIFICATION: THE ULTIMATE GUIDELINE FOR SECURING DATA
Modern businesses require incorporating personal data protection strategies to ensure customer satisfaction and business growth. In this respect, the European Union's General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) sets strict standards for maintaining data security....
GDPR Compliance Software: Boosting Business Efficiency
Handling large amounts of personal data has become a significant concern in today's digital landscape, necessitating a thorough understanding of the intricate legal framework, particularly within the European Union. An essential piece of legislation in this regard is...




