CCPA
CALIFORNIA CONSUMER PRIVACY ACT
The California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA) is the most comprehensive data privacy regulation in the United States, comparable to the EU’s General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR). It came into effect on January 1, 2020, and enforcement began on July 1, 2020, resulting in a significant global impact on businesses. The CCPA aims to protect the personal information of California residents by establishing strict rules for data access, collection, and storage. It guarantees businesses’ reliable handling of personal data and provides consumers with unmatched control over their information. By awarding individuals rights to access, delete, and opt out of the sale of their data, the CCPA empowers consumers and evens the playing field between businesses of different sizes. This legislation addresses the need for enhanced data privacy in today’s world, where personal information is vulnerable. The CCPA enhances privacy protections, allows consumers to determine how their data is used, and promotes transparency and accountability in data handling practices.

CERTIFICATION AND AUDITING SERVICES BY CERTPRO FOR CCPA
At CertPro, we recognize the importance of complying with the California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA) and the advantages of achieving CCPA compliance for organizations aiming to enhance their data privacy practices. We provide comprehensive support to businesses embarking on their CCPA compliance journey. Our team of experts will guide you throughout the process, ensuring that your data privacy policies and procedures align with the CCPA requirements. We will collaborate closely with your team to develop and implement a customized data privacy framework that addresses your business needs and complies with industry regulations.
WHY CHOOSE CERTPRO FOR CCPA CERTIFICATION AND AUDITING?
CertPro is a trusted and reputable partner for CCPA compliance services and audits. With our extensive experience in data privacy and protection, we have a deep understanding of the complexities associated with the California Consumer Privacy Act. Here are several compelling reasons why CertPro is the ideal choice to fulfill your CCPA compliance requirements:
| Factors | CertPro Advantage |
|---|---|
| Time to Certification | 4x faster than traditional approaches |
| Price | Competitive rates with flexible options |
| Process | Streamlined and efficient methodology |
| Expertise | 10+ years of industry experience |
CERTPRO’S COST-EFFECTIVE APPROACH TO CCPA CERTIFICATION
For CCPA compliance, the cost factor is an important consideration, taking into account various factors that influence expenses. At CertPro, we understand the importance of cost-effectiveness and strive to provide tailored and affordable solutions to meet your CCPA requirements. Here is an overview of our cost-effective approach to CCPA compliance:
| No. of employees | Timeline | Cost (approx.) |
| 1 – 25 | 4 weeks | 2500 USD |
| 25-100 | 6 weeks | 3500 USD |
| 100-250 | 6-8 weeks | 5000 USD |
| 250 plus | 8 weeks | Custom plans |
UNDERSTANDING THE CALIFORNIA CONSUMER PRIVACY ACT (CCPA)
The California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA) is a comprehensive privacy law enacted in California designed to strengthen consumer rights related to the collection or sale of personal information by businesses. Consumers have specific rights under the CCPA, including the ability to request access to, deletion of, or correction of their personal information as well as transparent disclosures about the personal information that businesses collect. Section 1798.140 of the CCPA mandates businesses to determine and disclose their business or commercial purpose.
Under CCPA Business Purpose, Using personal information by businesses or service providers for operational or notified purposes is permitted, provided it is reasonably necessary and proportionate. The CCPA outlines seven categories of business purposes, including auditing interactions with consumers, debugging and repair, security, specific short-term uses, internal research for tech development, performing services, and quality and safety maintenance and verification.
The CCPA also recognizes various services provided by businesses or service providers, such as account maintenance, customer service, order processing, customer information verification, payment processing, financing, advertising, marketing, analytics, and similar services.
Regarding CCPA Commercial Purpose, it pertains to activities that advance a person’s commercial or economic interests by facilitating transactions or exchanges of products, goods, property, information, or services. However, commercial purposes do not include speech recognized as noncommercial, such as political speech and journalism. While there is no specific list of commercial purposes, the distinction between commercial and business purposes may be unclear or overlap due to the broad definition of commercial purposes and the potential for dual purposes. Understanding the definitions and implications of business and commercial purposes is essential, as they are relevant in defining business entities, service providers, third parties, and research under the CCPA.
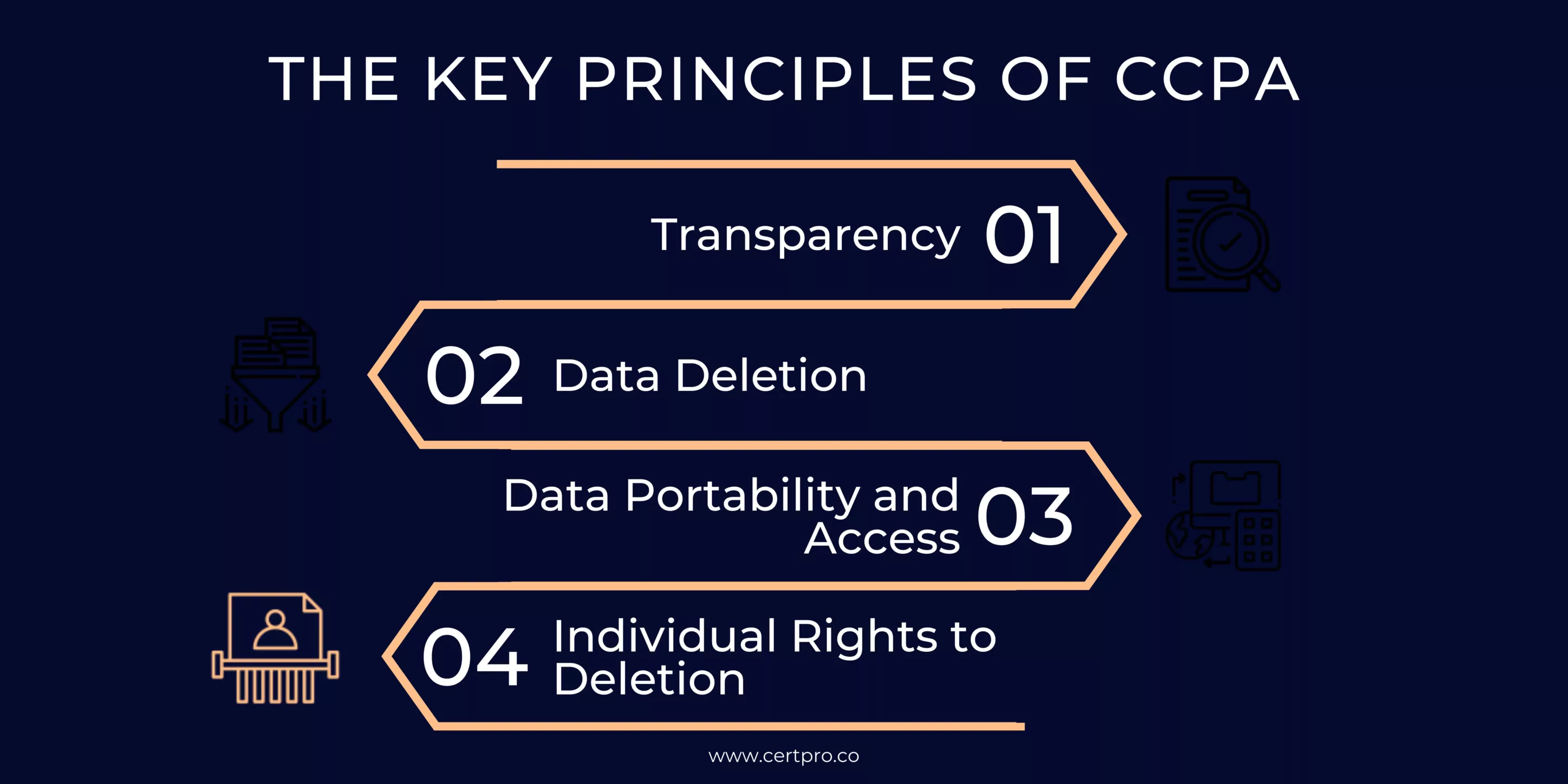
THE KEY PRINCIPLES OF CCPA
CCPA principles safeguard privacy, empower consumers, establish accountability, and promote responsible handling of personal data. The main principles include:
- Transparency: A business (controller) must actively provide consumers with information, including the categories of personal information to be collected, used, and shared with third parties. They should include this information in their privacy policy and ensure that it is updated at least once every 12 months.
- Data Deletion: Businesses must transmit deletion requests to their service providers, who face potential civil penalties under the CCPA.
- Data Portability and Access: The CCPA grants consumers the right to access and data portability. They can request their personal information from a business, including specific pieces and categories collected, shared with third parties, and obtained. Consumers also have the right to receive their personal information in a format that enables transmission to another organization. Businesses are obligated to respond to these requests within 45 days.
- Individual Rights to Deletion: The CCPA grants consumers the right to request the deletion of their personal information. Businesses must comply with these deletion requests from consumers.
RIGHTS UNDER THE CCPA
With accompanying regulations guiding compliance, the California Consumer Privacy Act of 2018 (CCPA) gives consumers increased control over the personal information that businesses collect. This significant legislation establishes new privacy rights for California consumers, such as:
- Right to Know: Consumers have a right to information about how businesses collect, use, and share their personal information.
- Right to Deletion: With a few exceptions, customers have the right to request the deletion of their personal information that businesses hold.
- Right to Opt-Out: Consumers decide on personal information sales or sharing, preserving privacy and asserting control over their data.
- Right to Non-discriminatory Treatment: Consumers are safeguarded against discrimination for exercising their CCPA rights, ensuring equal treatment regardless of their privacy choices.
Following voter approval of Proposition 24 in November 2020, the California Privacy Rights Act (CPRA) amended the CCPA and introduced additional privacy protections. Effective January 1, 2023, consumers now have more distant rights beyond those mentioned above, including:
- Right to Correct: Consumers have the right to have any inaccuracies in the personal information that businesses are keeping updated, ensuring data integrity and accuracy.
- Right to Limit the Use: Consumers have the right to restrict the use and disclosure of sensitive personal information collected about them, granting them added privacy and control.

A CCPA AUDIT
Conducting an audit is a valuable method to demonstrate your business’s adherence to the CCPA and dedication to data privacy. A CCPA audit is a systematic examination or review of processes or quality systems to ensure compliance with CCPA requirements. CCPA audits comprehensively assess your business operations, examining all aspects to identify any potential violations of the CCPA.
There are two main types of CCPA audits:
In the context of the CCPA, internal audits play a crucial role in ensuring compliance and data privacy. These audits involve various steps, including assessing the organization’s CCPA applicability, conducting risk assessments for all data held, understanding relevant privacy laws, educating the organization about CCPA, providing privacy and security training, making process recommendations, performing compliance audits, assisting with operational changes, acting as an in-house advisor, and engaging external consultants when needed. Internal audits help organizations proactively manage CCPA requirements and maintain compliance in an ever-evolving privacy landscape.
A third-party auditor performs an external audit to assess a business’s compliance with the privacy requirements outlined in the California Consumer Privacy Act. This audit verifies that the firm has implemented appropriate safeguards and practices to protect consumer personal information and ensure CCPA compliance.
OBTAINING CCPA COMPLIANCE: A STEP-BY-STEP GUIDE
Follow the six steps outlined below to understand the process of achieving CCPA compliance.
Step 1: Update Privacy Policy and Notices
Begin by reviewing your existing privacy policy and conducting a CCPA gap assessment. Update the policy to incorporate the new rights and requirements outlined in the CCPA. Assure that your revised privacy policy clearly outlines procedures for granting these rights under different circumstances. Additionally, make necessary updates to your privacy notices provided to consumers, offering more detailed information at the point of data collection regarding the use and processing of their data.
Step 2: Maintain a Sound Data Inventory
To ensure CCPA compliance, maintain a thorough data inventory that tracks all information processing activities. This inventory should encompass your business processes, products, devices, and software to handle consumer data. Classify the data according to CCPA requirements, identifying data types that are sold, shared with third parties, or used for marketing purposes. Additionally, record any rights requests related to specific data types in the inventory as evidence of your CCPA compliance efforts.
Step 3: Implement Data Rights Protocols
Ensure that the new consumer data rights outlined by the CCPA are at the forefront of your compliance efforts. Develop processes and protocols to address consumer requests when exercising their rights. For instance, if a consumer invokes their Right to Be Forgotten, your IT team should be well-informed about the data’s location and have streamlined procedures to dispose of the data and notify the consumer in a CCPA-compliant manner. Prepare protocols in advance to facilitate efficient and fully compliant handling of consumer rights requests.
Step 4: Strengthen Your Cybersecurity Stack
The CCPA mandates that all covered businesses implement “reasonable” security measures to safeguard personal data. Take a risk-based approach by assessing vulnerabilities across different data types, prioritizing the most at-risk areas, and enhancing systems and technology accordingly. While investing in a robust security and privacy platform for high-risk data may involve initial costs, failure to take appropriate measures could result in substantial fines and penalties in the event of a breach. Prioritize data protection to mitigate potential risks and ensure compliance with CCPA requirements.
Step 5: Audit Third-Party Processor Agreements
If your organization engages in collaborative arrangements with external entities for consumer data processing, storage, or transmission, it is crucial to audit and update those contracts for CCPA compliance. Partnering with a knowledgeable CCPA compliance expert can simplify this process by incorporating standard contractual language into your agreements, minimizing legal complexities. Ensure that your contracts address all aspects of CCPA compliance, including third-party data processing and collaboration on data rights requests.
Step 6: Continuous Internal Data Privacy Training
The CCPA requires organizations to provide training to individuals involved in consumer data handling, particularly those processing data rights requests. Training methods can include on-site classroom sessions, live virtual training, or standardized courses with materials and assessments. While the CCPA does not specify training frequency, it is advisable to conduct annual refresher sessions to ensure ongoing awareness and compliance.

HOW CCPA IS DIFFERENT FROM GDPR
The General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR), effective May 25, 2018, safeguards consumers’ data stored by businesses, granting powerful rights to EU citizens over their data. While the US lacks federal privacy legislation, state-level laws like the California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA) have emerged, promising GDPR-like protections and expanding rights for American internet users. While GDPR and CCPA aim to enhance individual control over personal data, they differ in approach. Here are the essential distinctions in scope, rights, and enforcement between these two laws:
- Scope: The GDPR has a broader territorial scope, applying to businesses processing the personal data of individuals in the European Union (EU). In In contrast, the CCPA applies to companies that collect the personal information of California residents, regardless of their location.
- Rights: Both laws provide individuals with rights over their data. The GDPR emphasizes rights such as access, rectification, erasure, and data portability. The CCPA focuses on the right to opt out of data selling, access, deletion, and non-discrimination.
- Enforcement: The GDPR imposes significant fines of up to 4% of global annual turnover for non-compliance. It also allows for regulatory enforcement. The CCPA imposes penalties per violation and enables private lawsuits for data breaches.
- Security Measures: The GDPR requires businesses to implement appropriate security measures to protect personal data. The CCPA does not explicitly outline specific security requirements but expects companies to implement reasonable security practices.
While both laws address privacy, the GDPR has a broader geographic reach and places greater emphasis on data protection rights, whereas the CCPA centers on individual control over personal information and data selling.
CCPA COMPLIANCE REQUIREMENTS
The requirements of CCPA compliance are structured to align with consumer rights over their personal data and encompass the following specific obligations for companies:
1. Process Inventory for Data Subject Access Requests, including the Right to Know:
Develop comprehensive workflows that provide visibility into the processes and activities connecting physical systems to data categories, purposes, and third-party sharing. It facilitates a transparent data flow, enabling efficient identification and evaluation of requested data.
2. Right to Opt-Out of Sales:
Match opt-out requests obtained from feeder systems with the reliable profile of an individual and their associated data, regardless of their location within the organization. Conduct data subject access request (DSAR) discovery reports to identify where the individual is utilizing the data.
3. Right to Access Data:
Streamline access requests by leveraging real-time insights on an individual’s relevant personal data, allowing for swift matching of the data with its intended purpose.
4. Right to Deletion:
Eliminate personally identifiable information from systems through remediation, employing deletion workflows. Utilize validation capabilities to evaluate data compliance with retention policies and establish an audit trail to confirm the removal or deidentification of the data.
5. Data Privacy Protection:
Automate the deployment of data security controls to mask personal data, ensuring protection against unauthorized access and monitoring for suspicious activities. Comply with data anonymization requirements by de-identifying data without impeding business operations.
BENEFITS OF CCPA COMPLIANCE
The benefits of CCPA compliance are as follows:
Easier Data Management: The CCPA offers several benefits for Easier, more affordable, and more scalable data management. Businesses can securely store, analyze, and derive insights from large volumes of data cost-effectively, leading to improved performance, reduced expenses, and the ability to leverage predictive analytics.
Enhanced Restricted Data Governance: The CCPA provides benefits in terms of improved governance of restricted data. Businesses can map their data to critical data elements, enabling effective validation and customization of workflows to ensure ongoing CCPA compliance even as the law evolves continuously.
Improved Customer Loyalty: The CCPA offers the advantage of enhanced customer loyalty. By anticipating customer needs and developing a strategic communication plan, businesses can effectively engage with customers, keeping their brand top of mind. Well-timed and informative communications are essential to building and nurturing ongoing customer relationships and fostering loyalty and trust.
Operationalize Regulatory Policies: The CCPA enables businesses to operationalize regulatory policies by establishing a centralized location. It includes defining and documenting policy, controls, governance processes, critical data elements, categories of data, subcategories, and data quality rules.
Mitigate Compliance Risk: The CCPA allows businesses to reduce compliance risk by effectively monitoring risk reports. By tracking and analyzing data risk, organizations can identify potential issues and take proactive measures to mitigate the business impact associated with non-compliance.
ELIGIBILITY FOR CCPA COMPLIANCE
The CCPA categorizes organizations into non-profit and for-profit groups, establishing specific jurisdiction criteria. Non-profit organizations are exempt from CCPA compliance, whereas for-profit organizations that collect data from California residents must comply.
The CCPA defines a California resident as an individual who resides within the state. Companies processing Personal Identifiable Information (PII) of Californians must comply with the CCPA, irrespective of their geographic location. However, companies face additional requirements, considering that not all can handle the financial burden associated with CCPA compliance.
Additional company criteria include:
- Annual revenue of $25 million or more
- Possession of a PII database with over 50,000 consumers, households, or devices
- More than half of annual revenue is derived from PII sales.
THE COST OF CCPA COMPLIANCE
Complying with the California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA) entails various costs that businesses must consider. The following four main cost categories, outlined in the Attorney General’s report, highlight the financial implications of CCPA compliance:
- Legal Costs: Businesses need legal counsel to assess the impact of the CCPA on their technical and operational plans, providing personalized interpretations of the law for their specific circumstances.
- Operational Costs: Establishing non-technical infrastructure and procedures to handle compliance obligations is necessary to meet CCPA requirements effectively.
- Technical Costs: Implementing technologies capable of handling consumer requests and incorporating features like an opt-out button on the website, primarily if the business sells personal information (PI), can incur expenses.
- Business Costs: CCPA may necessitate businesses to modify their existing business models and renegotiate agreements with service providers to ensure compliance with the privacy requirements.
While the exact compliance costs vary depending on the organization, the Attorney General’s report estimates that approximately 75% of California businesses will be subject to compliance, collectively resulting in around $55 billion in expenses. It represents about 1.8% of California’s 2018 Gross State Product. Businesses must assess these costs and allocate resources accordingly to ensure compliance with the CCPA.
CERTPRO’s ASSISTANCE IN CCPA COMPLIANCE
CertPro offers comprehensive auditing and consulting services to help your business achieve compliance with CCPA requirements. Their experienced professionals will assess your data protection practices, identify gaps, and provide guidance on implementing necessary measures to align with CCPA regulations. They can assist in developing and implementing privacy policies, procedures, and controls, as well as conducting data protection impact assessments. By partnering with CertPro, your business can enhance its ability to protect consumer privacy, mitigate risks, and demonstrate a commitment to consumer data privacy rights. CertPro’s services will enable you to navigate the complexities of CCPA compliance, foster trust with consumers, and ensure that your organization meets the required standards for handling personal information under CCPA regulations.
FAQ’s
WHAT ARE THE PENALTIES FOR NON-COMPLIANCE WITH CCPA?
Non-compliance with the CCPA can result in significant penalties. In the event of a data breach or violation, the California Attorney General can impose fines ranging from $2,500 to $7,500 per violation. Consumers also have the right to file private lawsuits, leading to potential statutory damages.
WHAT IS THE VALIDITY PERIOD OF CCPA COMPLIANCE?
CCPA compliance is an ongoing obligation for businesses that collect and process the personal information of California residents. There is no specific validity period mentioned in the CCPA. Organizations should maintain compliance as long as they handle personal data and operate within the scope of CCPA requirements.
IS CCPA COMPLIANCE ONLY REQUIRED FOR BUSINESS LOCATED IN CALIFORNIA?
No, CCPA compliance is not limited to businesses located in California. The CCPA applies to organizations that collect and process the personal information of California residents, regardless of the business’s physical location. If a company outside of California handles the personal information of Californians, it is still required to comply with the CCPA.
DOES CCPA COMPLIANCE IMPOSE ADDITIONAL COSTS ON SMALL BUSINESS?
CCPA compliance can impose financial burdens on smaller businesses that may not have the same resources as larger companies. However, the law aims to level the playing field by requiring all businesses to comply with the same standards, regardless of size.
CAN COMPLIANCE WITH THE CCPA HELP TO IMPROVE DATA PRIVACY AND CONSUMER TRUST?
Yes, CCPA compliance helps businesses handle personal data responsibly and gives consumers greater control over their information. By demonstrating compliance, organizations can enhance data privacy practices, build trust with consumers, and mitigate reputational and legal risks.
HOW DOES THE NIST CYBERSECURITY FRAMEWORK FUNCTION, AND WHY IS IT IMPORTANT?
Emerging cyber threats make cybersecurity an essential consideration for organizations handling and managing data. In this regard, the NIST cybersecurity framework applies to improving your cybersecurity program. It is a set of guidelines that helps improve your...
UNDERSTANDING ISO 42001: A GUIDE FOR RESPONSIBLE AI MANAGEMENT SYSTEMS
The invention of artificial intelligence (AI) has changed the operational processes of many industries. However, the rapid growth of technology increases ethical, security, and privacy-related concerns. Therefore, the International Organization for Standardization...
EUROPEAN UNION’S ARTIFICIAL INTELLIGENCE ACT: HOW THIS GROUNDBREAKING LAW AFFECTS YOUR BUSINESS
Nowadays, Artificial Intelligence (AI) is transforming our lives exceptionally well. AI is now streamlining healthcare services, providing virtual assistance, and fulfilling queries. Technologies have boons and curses. Similarly, AI creates many concerns about...




















