In the digital age, where personal data has become an invaluable asset, safeguarding its privacy and security is paramount. Data Processing Agreements emerge as essential tools in this endeavor. A DPA is a legally binding contract that delineates the terms governing the processing, sharing, and protection of personal data between various parties.
It plays a pivotal role in ensuring compliance with data protection regulations such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) in the European Union. They establish a framework that clarifies the roles and responsibilities of data controllers, who determine data processing purposes, and data processors, who handle data on behalf of controllers.
As this article delves deeper into the realm of DPA, it becomes evident that these agreements are not mere formalities but ethical commitments to data subjects. The data processing agreement champions responsible data management, secure data handling practices, and a culture of transparency. In an era where data is both a strategic asset and a sensitive commodity, DPAs offer a beacon of assurance for individuals entrusting their information to organizations worldwide.
WHAT IS A DATA PROCESSING AGREEMENT?
A Data Processing Agreement is a formal agreement between a data controller and a data processor. It can also be an arrangement between a data processor and a subprocessor or between a controller and a joint controller. The DPA specifies who the data subjects are, what type of information is processed, what categories of data are processed, who collects the client’s personal data, how it is treated, where it is stored, how long it is stored, how it can be retrieved, deleted, processed, protected, and what kind of measures the parties should take to prevent data breaches.
Organizations that handle the personal data of European Union data subjects must have a Data processor agreement in place. Article 28 of the EU GDPR data processing agreement specifies the clauses that must be included in such agreements. Failure to follow these criteria will result in severe fines and penalties. It can be included as an Appendix to the underlying service contract, such as the SAAS contract, and so on. The terms of such agreements should specifically state which activities relate to the services offered. It is a legally binding document that applies to anyone. This document cannot stand alone and must refer to specific underlying agreements. There will be some cross-reference between the DPA and the underlying contract.
The GDPR data processing agreement sets numerous requirements for those who wish to acquire and utilize personal data. It governs the specifics of data processing, such as:
1. The processing’s scope and purpose
2. The interaction between these actors
3. Each party’s duties under the regulation
WHY IS A DATA PROCESSING AGREEMENT REQUIRED?
Data Protection Agreements are needed for several critical reasons, primarily revolving around ensuring the privacy, security, and legal compliance of personal data.
Here’s why DPAs are essential:
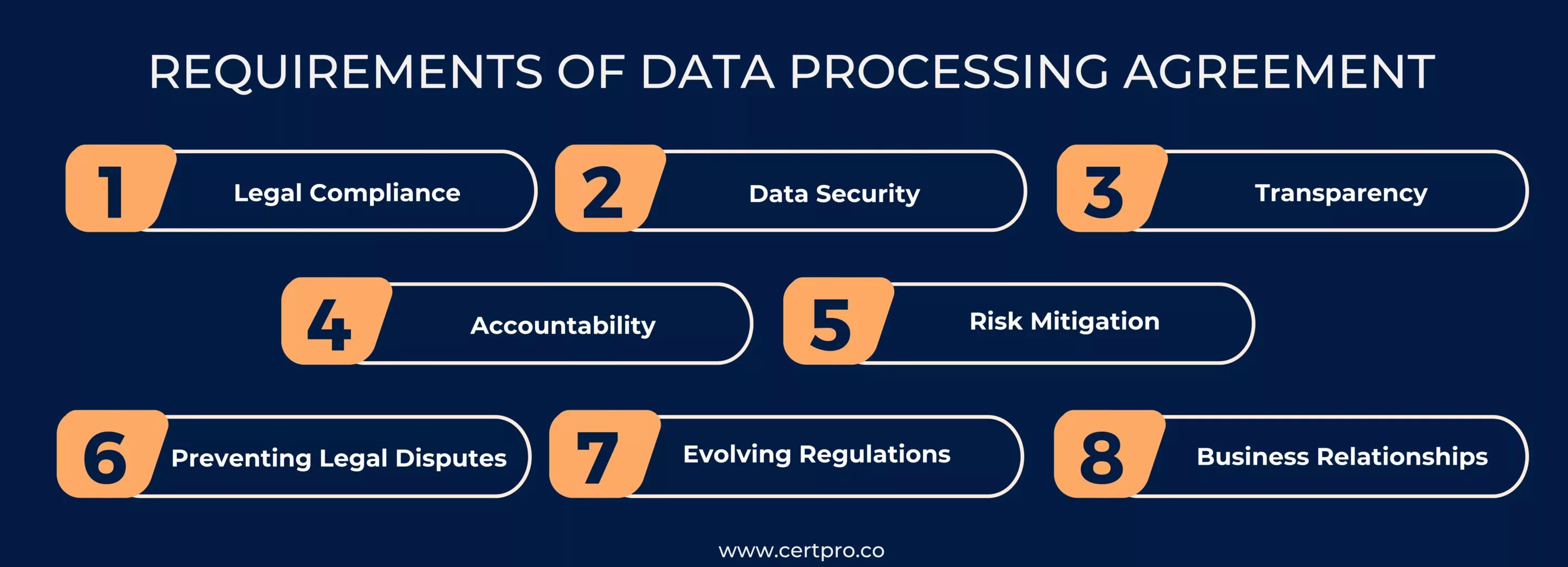
1. Legal Compliance: Organizations that process personal data must meet specific legal requirements for data handling, and the data processing agreement outlines the necessary measures to achieve compliance.
2. Data Security: It defines the security measures that need to be implemented to protect personal data from breaches, unauthorized access, or loss. This is especially important given the increasing frequency and severity of data breaches.
3. Transparency: It promotes transparency by clearly articulating how personal data will be processed, who will have access to it, and for what purposes. This transparency is crucial for building trust with data subjects.
4. Accountability: It establishes accountability by outlining the roles and responsibilities of data controllers and processors. This ensures that all parties involved understand their obligations and act accordingly.
5. Risk Mitigation: It helps mitigate the risks associated with data processing. By defining procedures, responsibilities, and security measures, organizations can reduce the likelihood of data breaches and other data-related incidents.
6. Preventing Legal Disputes: By clearly defining the terms and conditions of data processing, It helps prevent misunderstandings between parties and potential legal disputes that could arise from data mishandling.
7. Evolving Regulations: Data protection laws are evolving, and they provide a mechanism for organizations to adapt to changing legal requirements and best practices.
8. Business Relationships: In cases where data is shared between different organizations, It serves as a contractual basis for establishing data-sharing partnerships.
WHAT SHOULD BE INCLUDED IN THE DATA PROCESSING AGREEMENT?
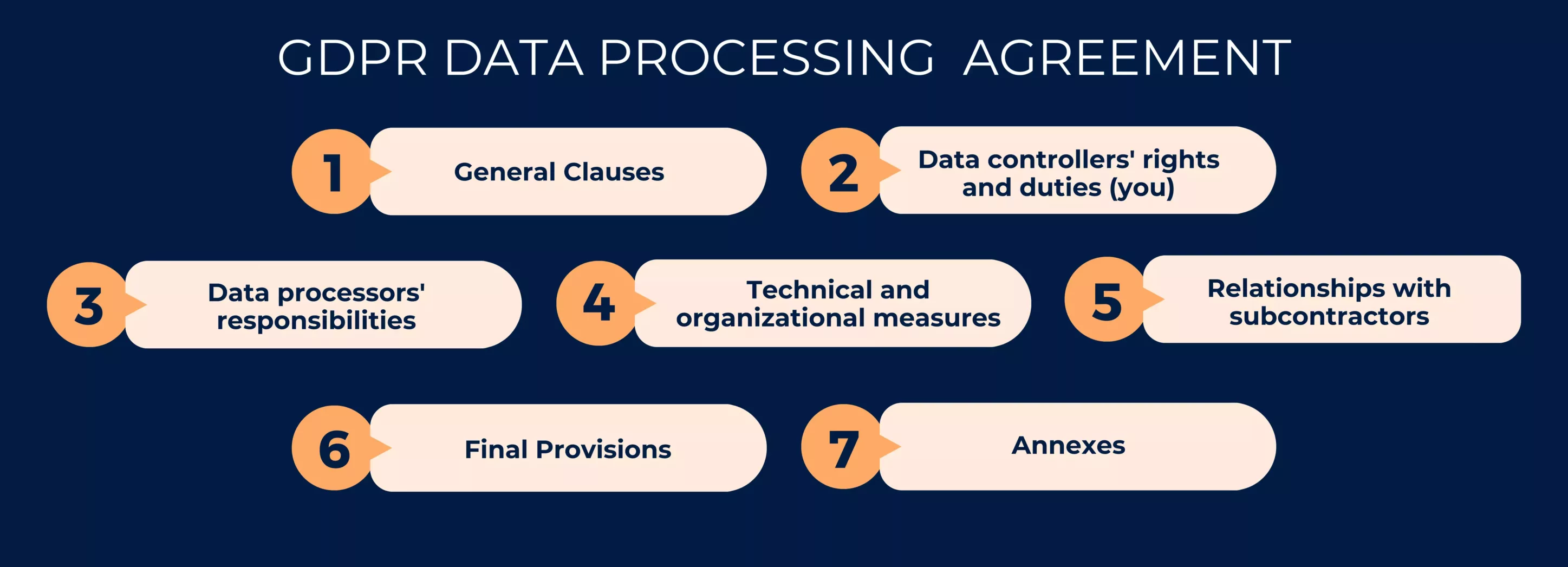
1. General Clauses: It contains the terms and conditions agreed upon by both parties in the contract. This includes all activities required to process the data provided by the data’s owner, such as patients, insurance clients, and staff.
2. Data controllers’ rights and duties (you): It should additionally incorporate the following provisions into your duties as the data controller:
- You are responsible for implementing a lawful data process and upholding data subjects’ rights
- You are in charge of issuing data processing instructions.
3. Data processors’ responsibilities: GDPR data processing agreement Articles 28–36 outline data processor duties. They include, among other things:
- It is necessary to offer proper information security.
- Sub-processors should not be used without your prior agreement.
4. Technical and organizational measures: It must cover all of the preventive and security measures that the data controller must take when managing personal data in order to avoid third-party attacks and data breaches. The following precautions should be implemented:
- The collected personal information will be encrypted and pseudonymized.
- During data processing, confidentiality, integrity, availability, and resilience must be ensured.
5. Relationships with subcontractors:This section elaborates on the interaction between the primary data processor and sub-processors
Here’s what you should include in this section of the agreement:
- In order to involve sub-processors, the data processor must obtain the data controller’s express approval.
6. Final Provisions:The Final Clauses section consists of other necessary information and shall state that both parties must agree to any modifications of the contract.
7. Annexes:The contractual agreements, such as technical and organizational measures and a list of sub-processors, must be included in the annexes section.
TIPS FOR NEGOTIATING DATA PROCESSING AGREEMENT
Negotiating a Data Processing Agreement requires careful attention to legal requirements, data security, and mutual understanding.
Here are some tips to guide successful DPA negotiations:
- Prepare Thoroughly: Understand your organization’s data processing needs, the roles of each party, and the data involved.
- Legal Expertise: Involve legal professionals knowledgeable about data protection laws to ensure compliance.
- Clear Definitions: Define terms like “personal data,” “processing,” and “data subject” to avoid confusion.
- Mutual Goals: Emphasize data security, privacy, and legal compliance as shared objectives.
- Balanced Terms: Strive for an equitable distribution of responsibilities, liabilities, and data protection measures.
- Data Minimization: Agree on collecting and processing only necessary data to minimize risks.
- Data Breach Procedures: Define clear steps for reporting and responding to data breaches.
- Data Subject Rights: Outline how data subjects can exercise their rights and how the processor will assist.
- Security Measures: Specify technical and organizational measures to protect personal data.
- Subprocessors: Address subcontractor involvement and their adherence to data protection standards.
- Data Transfers: If relevant, determine mechanisms for lawful cross-border data transfers.
- Term and Termination: Clearly define the agreement’s duration and conditions for termination.
- Flexibility for Changes: Include provisions for adjusting the Data processor agreements as regulations evolve.
- Governing Law: Specify the governing law and jurisdiction for dispute resolution.
- Open Communication: Foster transparent communication and collaboration throughout negotiations.
- Data Subject Impact: Consider the impact of data processing on individuals and how their privacy will be protected.
- Audit Rights: Agree on procedures for auditing data processing practices to ensure compliance.
- Documentation: Keep records of negotiations, amendments, and final agreements.
- Regular Review: Set a schedule for reviewing and updating it to stay aligned with changing regulations.
Negotiating, It is not just a legal process; it’s about building trust and ensuring responsible data handling. Effective negotiations result in an agreement that safeguards personal data.
SAFEGUARDING DATA PROCESSING THROUGH DPA
In the contemporary landscape of data-driven operations, safeguarding personal information has become paramount. Data processor agreements, binding contracts that delineate the terms governing data handling, play a pivotal role in ensuring adherence to stringent data protection regulations like the GDPR. By clarifying the roles and responsibilities of data controllers and processors, It fosters transparency and trust.
Addressing data breach protocols, data subject rights, security measures, and subprocessor collaborations, well-structured It serves as a shield against unauthorized access and breaches. Beyond compliance, they signify an organization’s commitment to ethical data practices, bolstering confidence among data subjects.
FAQ
WHAT IS THE IMPORTANCE OF DATA PROCESSING AGREEMENTS IN THE DIGITAL AGE?
WHAT COMPONENTS SHOULD BE INCLUDED IN A DATA PROCESSOR AGREEMENT?
HOW DOES A DATA PROCESSING AGREEMENT ENHANCE TRANSPARENCY AND TRUST?
WHAT ARE THE CONSEQUENCES OF NOT HAVING A DATA PROCESSING AGREEMENT?
HOW SHOULD ORGANIZATIONS NEGOTIATE A DATA PROCESSING AGREEMENT EFFECTIVELY?

About the Author
GANESH S
Ganesh S, an expert in writing content on compliance, auditing, and cybersecurity, holds a Bachelor of Arts (BA) in Journalism and Mass Communication. With a keen eye for detail and a knack for clear communication, Ganesh excels in producing informative and engaging content in the fields of compliance, auditing, and cybersecurity, with particular expertise in ISO 27001, GDPR, SOC 2, HIPAA, and CE Mark.
HOW TO CONDUCT A GDPR AUDIT FOR MY BUSINESS?
The General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) is vital for today's digital landscape. It is a cornerstone for safeguarding people's privacy rights in the European Union (EU). Therefore, organizations dealing with EU residents' data must follow these GDPR rules....
GDPR DATA BREACH NOTIFICATION: THE ULTIMATE GUIDELINE FOR SECURING DATA
Modern businesses require incorporating personal data protection strategies to ensure customer satisfaction and business growth. In this respect, the European Union's General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) sets strict standards for maintaining data security....
GDPR Compliance Software: Boosting Business Efficiency
Handling large amounts of personal data has become a significant concern in today's digital landscape, necessitating a thorough understanding of the intricate legal framework, particularly within the European Union. An essential piece of legislation in this regard is...




