In our digital age, “data privacy” and “data security,” often used interchangeably, represent distinct aspects of online information protection. Underpinning data privacy are consent and transparency, which safeguard individuals’ rights over personal information. In contrast, data security relies on encryption and access controls to protect data from unauthorized access or damage. Recognizing the differences between data privacy vs. data security is crucial for navigating the complexities of data protection in our data-driven world.
Data Privacy is fundamentally concerned with the protection of individuals’ rights and freedoms regarding their personal information. It revolves around principles such as consent, transparency, and the control individuals should have over the collection, processing, and sharing of their data. On the other hand, Data Security primarily focuses on safeguarding data from unauthorized access, disclosure, alteration, or destruction. It encompasses technical and procedural measures such as encryption, access controls.
This article will delve deeper into these distinctions, exploring the core components of privacy and security, their objectives, and their roles in the evolving landscape of data protection. Understanding these differences is pivotal to navigating the complexities of data governance and ensuring a balanced approach to data protection in our data-driven world.
WHAT IS DATA PRIVACY?
Data privacy, in essence, is a fundamental concept that centers on the protection of individuals’ rights and freedoms concerning their personal information within the context of our rapidly evolving digital world. In the context of digital technology and the internet, data privacy aims to ensure that people exercise some degree of control over how others gather, process, share, and use their personal data.
Some of the key principles that underpin data privacy include the necessity for individuals to provide clear and informed consent before their data is collected and processed, the importance of transparency regarding how organizations handle data, the principle of data minimization, which advocates for the collection of only necessary data, and the notion of purpose limitation, which dictates that data should only be utilized for the specific purposes for which it was originally gathered.
In terms of legal frameworks, various data privacy regulations and laws have been instituted worldwide to enforce these principles. Prominent examples include the European Union’s General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR), the California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA), and the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) within the healthcare industry. These regulations impose stringent requirements on organizations regarding the responsible handling of personal data and stipulate severe penalties for non-compliance.
In conclusion, data privacy stands as a cornerstone concept championing the safeguarding of individual privacy rights in the digital age. It erects a framework for responsible data handling, striving to strike a balance between the advantages brought forth by data-driven innovation and the preservation of personal liberties.
WHAT IS DATA SECURITY?
Data security is a multifaceted concept at the heart of preserving the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of information in a world characterized by digital connectivity and constant data exchange. It encompasses a comprehensive range of practices, protocols, technologies, and measures designed to protect data from unauthorized access, disclosure, alteration, or destruction, thereby ensuring that sensitive information remains safeguarded and uncorrupted.
Central to data security are access controls that serve as digital gatekeepers, determining who can access specific data and under what conditions. These controls often involve the use of authentication methods like usernames and passwords, biometrics, and multi-factor authentication to verify the identity of users seeking access.
Encryption is another vital component of data security, whereby data is transformed into an unreadable format using complex algorithms. Only individuals with the appropriate decryption keys can decipher and access the information. Firewalls and Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS) play a crucial role in data security by monitoring network traffic for suspicious activities and blocking or alerting administrators to potential threats.
In conclusion, data security is a multifaceted discipline indispensable to safeguarding data against an ever-evolving array of threats. It encompasses technical, procedural, and human elements, all working in concert to ensure the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of information. In a world where data is a prized asset, robust data security measures are paramount to protecting both individual privacy and the interests of organizations and governments.
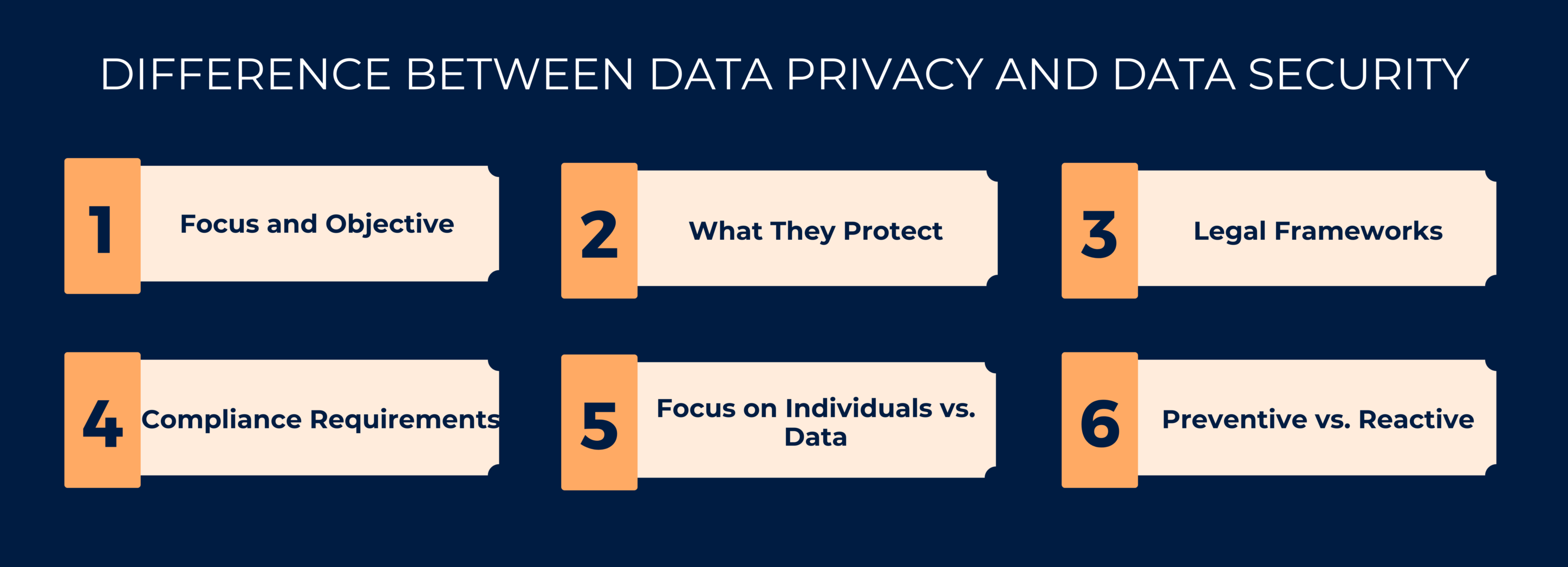
DIFFERENCE BETWEEN DATA PRIVACY AND DATA SECURITY
Data privacy vs. data security are two critical aspects of protecting information, but they have distinct focuses and objectives in safeguarding data in our digital age. The key differences between data privacy and data security are:
1. Focus and Objective:
Data Privacy: The primary focus of data privacy is protecting individuals’ rights and freedoms concerning their personal data.
Data Security: Data security primarily aims to protect data from unauthorized access, disclosure, alteration, or destruction.
2. What They Protect:
Data Privacy: Data privacy protects the personal information of individuals, such as their names, addresses, email addresses, and other identifiable information.
Data Security: Data security protects all forms of data, including personal data, intellectual property, financial records, and more.
3. Legal Frameworks:
Data Privacy: Data privacy is enforced through regulations and laws, such as GDPR in Europe, CCPA in California, and HIPAA in the healthcare industry.
Data Security: Industry standards and best practices often guide data security, but specific laws typically do not govern it.
4. Compliance Requirements:
Data Privacy: Organizations must comply with data privacy regulations, which often require them to appoint Data Protection Officers and conduct Data Protection Impact Assessments.
Data Security: While there are no specific compliance requirements for data security, organizations are encouraged to follow recognized security frameworks and standards to adequately protect their data.
5. Focus on Individuals vs. Data:
Data Privacy: Data privacy is inherently about individuals’ rights and their control over their personal information.
Data Security: Data security is primarily concerned with protecting the data itself, regardless of whether it belongs to individuals.
6. Preventive vs. Reactive:
Data Privacy: Data privacy is often more preventive in nature. It emphasizes upfront measures like obtaining consent and implementing privacy by design to prevent privacy violations.
Data Security: Data security is more reactive in nature. It involves measures like intrusion detection and incident response.
BEST PRACTICES FOR ENSURING DATA PRIVACY AND DATA SECURITY
In an age where data is the lifeblood of businesses and personal information is constantly at risk, robust data privacy vs. data security practices have never been more critical. Organizations and individuals alike must adopt best practices to protect sensitive information, maintain trust, and stay compliant with evolving regulations.
Data Privacy Best Practices:
- Informed Consent: Begin by obtaining explicit and informed consent from individuals before collecting and processing their data.
- Transparency: Maintain transparency in data practices. Provide easily accessible privacy policies and notices that explain how data is collected, used, and shared, keeping individuals informed about any changes.
- Data Minimization: Collect only the data that is necessary for a specific purpose. Avoid gathering excessive information to reduce the risk of misuse.
- Purpose Limitation: Ensure that data is used solely for the purpose for which it was collected.
- Data Subject Rights: Respect individuals’ rights to access their data, correct inaccuracies, and request the deletion of their information.
Data Security best practices:
In a recent survey, it was discovered that 63% of Americans would decline the opportunity to share their personal data in exchange for receiving advertisements related to a free service.
Therefore, it is advisable to implement the following best practices:
- Minimizing Data Collection: Ensure that your organization has appropriate policies in place to guarantee that only essential data is collected.
- Engaging Users: Many users are well-versed in privacy concerns and are open to receiving transparent information about how your organization uses and stores their data.
- Auditing Your Data: Achieving data privacy starts with a comprehensive understanding of the data you possess, how it is employed, and where it is stored.
By adhering to privacy and security practices, you can ensure that your organization respects privacy, aligns with regulations, and maintains the trust of your customers in an era where data privacy is paramount.
NAVIGATING THE NEXUS OF DATA PRIVACY AND DATA SECURITY
While the terms data privacy vs. data security are often used interchangeably, their distinctions are pivotal in understanding their roles and responsibilities in the realm of information protection.
Data Privacy is the guardian of individual rights, emphasizing consent, transparency, and responsible data handling. It is about respecting the autonomy of individuals and ensuring their personal information is used ethically and lawfully. Data Security, on the other hand, is the fortress of data itself, safeguarding it from a myriad of threats. It employs technical and procedural measures like encryption, access controls, and intrusion detection to shield data from unauthorized access, disclosure, or tampering.
Recognizing the differences between privacy and security is essential for organizations and individuals alike. While data privacy champions the rights of individuals, data security fortifies the very data upon which modern society relies. As we journey further into the digital frontier, the symbiotic relationship between data privacy vs. data security becomes even more critical. It is not a mere choice but an imperative for a safer, more ethical, and more secure digital future.
SIMILARITIES BETWEEN DATA SECURITY AND DATA PRIVACY
1. Both Help in Data Protection: Active data protection is the shared objective of data security and privacy. Because both of these phrases are ultimately concerned with maintaining the security and integrity of data, they are frequently used interchangeably. The desire for ethical and safe data management is evident in the widespread concern that data be used for the intended purpose, regardless of the source—individual consumers or corporations.
2. Both Require Similar Rules: Ensuring the privacy and security of data requires strict adherence to set rules that govern how businesses collect, use, and distribute data. These rules act as a vital framework, keeping sensitive data safe from potential breaches and misuse as well as preventing unauthorized access. They essentially serve as a barrier against information leaks, preserving data integrity and the public’s faith that businesses will handle it appropriately.
3. Both Are Required to Create a Strong Data Policy: Data privacy and security measures must be included in any comprehensive data policy that a business creates. The combination of these two elements is necessary since ignoring one of them makes it more difficult to address the dangers and changing issues related to data management. To put it simply, a thorough strategy that takes into account both data security and privacy is essential for handling the complex issues that come up in the field of data governance.
FAQ
ARE DATA PROTECTION AND DATA SECURITY TERMS INTERCHANGEABLE?
No, they are not interchangeable. Data privacy and data security are related but distinct concepts. Data privacy addresses the ethical and legal aspects of data handling, while data security deals with the technical and procedural measures to protect data.
HOW DO INDIVIDUALS CONTRIBUTE TO PRIVACY AND SECURITY EFFORTS?
Individuals can contribute by practicing good online hygiene, using strong passwords, being cautious about sharing personal information, and staying informed about data protection rights and risks.
WHAT ARE THE DIFFERENCE BETWEEN DATA PRIVACY AND DATA SECURITY?
Data protection involves safeguarding individuals’ personal information, respecting their privacy rights, and complying with regulations. Data security, on the other hand, focuses on safeguarding data from breaches, unauthorized access, and cyber threats through technical and procedural measures.
HOW DOES DATA PROTECTION AND DATA SECURITY AFFECT AN ORGANIZATION’S REPUTATION?
Failure to uphold data privacy and security can damage an organization’s reputation. A data breach or privacy violation can erode trust among customers and stakeholders.
HOW DO ORGANIZATIONS ENSURE DATA PRIVACY VS. DATA SECURITY COMPLIANCE SIMULTANEOUSLY?
Organizations can achieve compliance by implementing a combination of technical safeguards (data security measures) and privacy practices (obtaining consent, data transparency, and data governance).

About the Author
RAGHURAM S
Raghuram S, Regional Manager in the United Kingdom, is a technical consulting expert with a focus on compliance and auditing. His profound understanding of technical landscapes contributes to innovative solutions that meet international standards.
HOW DOES THE NIST CYBERSECURITY FRAMEWORK FUNCTION, AND WHY IS IT IMPORTANT?
Emerging cyber threats make cybersecurity an essential consideration for organizations handling and managing data. In this regard, the NIST cybersecurity framework applies to improving your cybersecurity program. It is a set of guidelines that helps improve your...
UNDERSTANDING ISO 42001: A GUIDE FOR RESPONSIBLE AI MANAGEMENT SYSTEMS
The invention of artificial intelligence (AI) has changed the operational processes of many industries. However, the rapid growth of technology increases ethical, security, and privacy-related concerns. Therefore, the International Organization for Standardization...
EUROPEAN UNION’S ARTIFICIAL INTELLIGENCE ACT: HOW THIS GROUNDBREAKING LAW AFFECTS YOUR BUSINESS
Nowadays, Artificial Intelligence (AI) is transforming our lives exceptionally well. AI is now streamlining healthcare services, providing virtual assistance, and fulfilling queries. Technologies have boons and curses. Similarly, AI creates many concerns about...