In recent years, cloud data security has evolved from being a convenient data storage solution to a fundamental component of modern business operations. Organizations increasingly rely on cloud infrastructure not only for data storage but also for critical business applications, data processing, and collaboration. This expansion of cloud usage has brought about a paradigm shift in the way data is accessed, shared, and protected.
However, as cloud adoption has surged, so too have the threats and vulnerabilities associated with it. Cybercriminals, fueled by the potential for financial gain and the allure of valuable data, are constantly devising new and sophisticated attack methods to breach cloud security. This evolving threat landscape poses a significant challenge to organizations seeking to safeguard their data in the cloud.
As businesses embark on their digital transformation journey, understanding and fortifying data security are more critical than ever. This article delves into the intricacies of cloud data security, explores common issues, and outlines strategies for mitigating risks and challenges, empowering organizations to harness the full potential of cloud computing securely.
UNDERSTANDING CLOUD DATA SECURITY
COMMON CLOUD COMPUTING SECURITY ISSUES
KEY SECURITY RISKS IN CLOUD COMPUTING
CRUCIAL CLOUD DATA PROTECTION MEASURES
WHY COMPANIES NEED CLOUD DATA SECURITY?
WHAT ARE THE 5 COMPONENTS OF DATA SECURITY IN CLOUD COMPUTING?
NAVIGATING THE CLOUD SECURITY MAZE: ADDRESSING KEY CHALLENGES
UNDERSTANDING CLOUD DATA SECURITY
Cloud data security is the practice of protecting data stored, processed, and transmitted within cloud environments. It is a multifaceted approach aimed at ensuring the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of data while preventing unauthorized access and data breaches. Let’s delve deeper into the critical aspects of data security.
Confidentiality: Protecting the confidentiality of data means ensuring that only authorized individuals or systems can access it. Encryption is a fundamental technique used in data security to encode data so that it remains unreadable to unauthorized parties. Additionally, access controls, such as role-based access control (RBAC), are implemented to restrict data access based on user roles and permissions.
Integrity: Data integrity ensures that information remains accurate and trustworthy throughout its lifecycle. Cloud data security measures include mechanisms to detect and prevent unauthorized modifications, corruption, or tampering with data. This is often achieved through data checksums, digital signatures, and regular integrity checks.
Availability: Cloud services are expected to provide uninterrupted access to data. Ensuring data availability involves implementing redundancy, failover mechanisms, and disaster recovery plans. This safeguards against service outages, hardware failures, or natural disasters that could otherwise lead to data unavailability.
Authentication and Authorization: Strong authentication and authorization mechanisms are fundamental to data security. Users and systems must be verified before accessing data or cloud resources. Multi-factor authentication (MFA) is commonly used to add an extra layer of security by requiring users to provide multiple forms of identification.
Data Classification and Lifecycle Management: Not all data is of equal importance, and data security requires classifying data based on its sensitivity. Organizations must establish data retention policies and define how data is stored, archived, and eventually deleted when it’s no longer needed. Proper data lifecycle management helps reduce the risk of data breaches.
COMMON CLOUD COMPUTING SECURITY ISSUES
Cloud computing has revolutionized the way businesses operate by offering flexibility, scalability, and cost-effectiveness. However, along with these benefits come significant concerns and challenges that organizations must address. One of the most prominent concerns in cloud computing is the risk of data breaches, exemplified by high-profile incidents like the 2019 Capital One breach. These incidents serve as stark reminders of the vulnerability of cloud-stored data to unauthorized access.
Data breaches are not the only threat organizations face when utilizing cloud services. Another important problem that can have serious repercussions without effective backup and recovery systems in place is accidental data deletion or corruption, as demonstrated by Microsoft’s 2020 data loss disaster.
A few mentions of cloud computing security issues:
Data Breaches: Perhaps the most prominent concern in cloud computing is the risk of data breaches. High-profile incidents like the 2019 Capital One breach serve as stark reminders of the vulnerability of cloud-stored data to unauthorized access.
Incident Example: In 2017, the Equifax data breach exposed the personal information of over 143 million individuals due to a vulnerability in their cloud-based web application.
Data Loss: Accidental deletion or corruption of data is another significant issue. Without robust backup and recovery mechanisms in place, data loss incidents can have severe consequences.
Incident Example: In 2020, Microsoft suffered a data loss incident that resulted in the permanent deletion of a significant number of customer data files stored on its servers.
Compliance Challenges: Many organizations are subject to specific regulatory requirements, such as GDPR, HIPAA, or PCI DSS. Ensuring compliance within cloud environments can be a complex endeavor that demands careful planning and implementation.
Incident Example: In 2018, Uber faced repercussions for failing to disclose a data breach promptly, which violated multiple state and federal laws.
KEY SECURITY RISKS IN CLOUD COMPUTING
The adoption of cloud computing has revolutionized after the cloud computing security risks increases the way organizations store, process, and manage their data. While the cloud offers numerous benefits, such as scalability and cost-efficiency, it also introduces a host of security risks that organizations must vigilantly address. This article focuses on key security risks associated with cloud computing, shedding light on real-world incidents that serve as stark reminders of the potential consequences of inadequate security measures.
Inadequate access controls, shared infrastructure in multi-tenant environments, and third-party vulnerabilities are among the primary concerns that can lead to data breaches and other security incidents. Understanding these risks and learning from historical examples is essential for organizations striving to harness the power of the cloud while safeguarding their sensitive information.
Inadequate Access Controls: Weak access management can result in unauthorized individuals gaining access to sensitive data. Implementing strong access controls and adhering to the principle of least privilege are essential.
Incident Example: The 2014 iCloud celebrity photo hack demonstrated the risks associated with weak access controls when celebrities’ private photos were accessed and leaked to the public.
Shared Infrastructure: In multi-tenant cloud environments, the actions of one user can potentially impact others. This shared infrastructure can lead to data leakage if not properly isolated and secured.
Incident Example: The 2017 AWS S3 data breach occurred due to misconfigured access controls, leading to the exposure of sensitive data from various organizations.
Third-Party Vulnerabilities: Organizations often rely on third-party cloud service providers. While these providers offer robust security measures, dependencies on external entities can expose organizations to vulnerabilities beyond their control.
Incident Example: The 2020 SolarWinds supply chain attack highlighted the risks of third-party vulnerabilities when hackers compromised SolarWinds’ software updates, affecting numerous organizations.
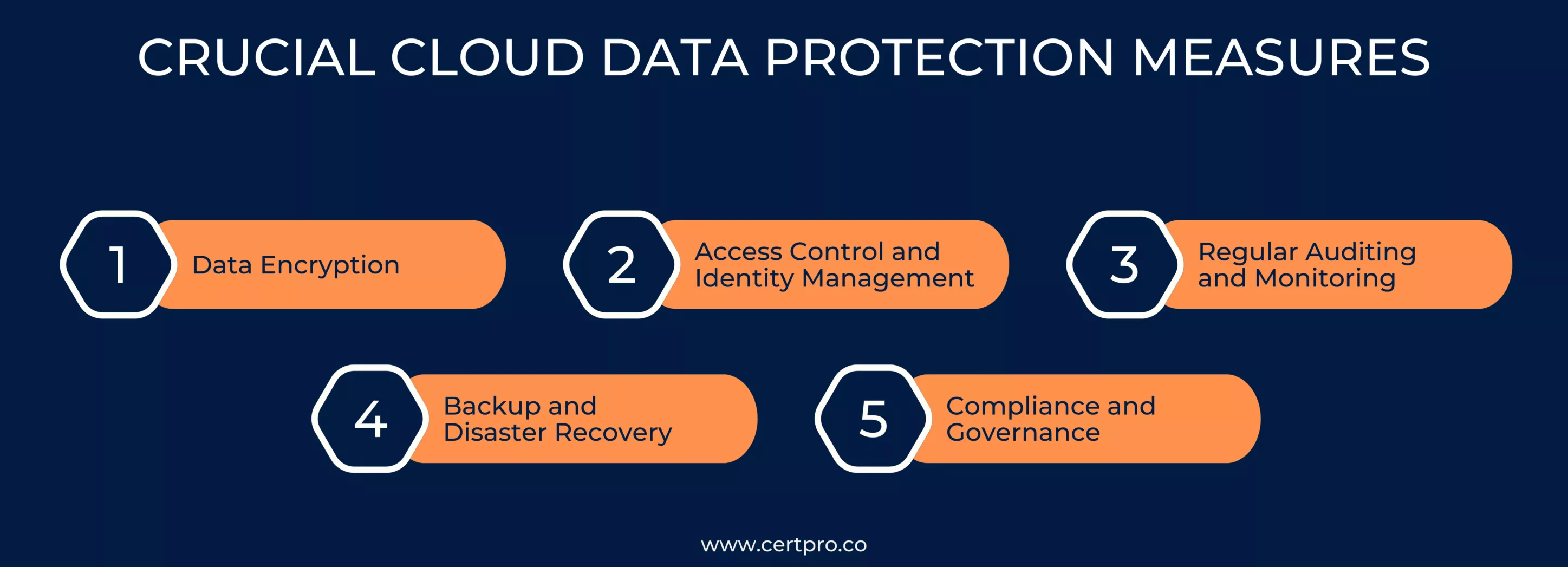
CRUCIAL CLOUD DATA PROTECTION MEASURES
To address these issues and mitigate security risks effectively, organizations must adopt a comprehensive approach to cloud data protection. Here are crucial measures to consider:
Data Encryption: Encrypt data both in transit and at rest using strong encryption algorithms. Encryption serves as a fundamental safeguard against data breaches.
Access Control and Identity Management: Implement stringent access controls to ensure that only authorized users can access data. Incorporate multi-factor authentication to enhance security.
Regular Auditing and Monitoring: Continuously monitor cloud environments for unusual activities and conduct regular security audits to identify vulnerabilities and threats promptly.
Backup and Disaster Recovery: Establish reliable backup and disaster recovery strategies to minimize data loss in the event of an incident. Regularly test these procedures to ensure their effectiveness.
Compliance and Governance: Understand and adhere to relevant regulatory requirements specific to your industry. Develop strong governance practices to maintain compliance and enforce security policies.
WHY COMPANIES NEED CLOUD DATA SECURITY?
In the current era of vast amounts of data, businesses are constantly creating, gathering, and storing a variety of data types, from extremely sensitive customer data to behavioral and marketing analytics. Organizations are adopting cloud services in order to facilitate remote or hybrid workforces, improve agility, and have faster time-to-market as the demand for effective data access, administration, and analysis increases.
Security teams need to reevaluate how they are protecting cloud data because the traditional network boundary is quickly disappearing. Companies now have to worry about protecting data and controlling access across a variety of environments since data and apps are no longer restricted to physical data centers and there is an increase in remote work. It is necessary to reconsider security strategies in order to maintain data integrity and access control as workforce arrangements and data storage practices change.
WHAT ARE THE 5 COMPONENTS OF DATA SECURITY IN CLOUD COMPUTING?
1. Verification and Control of Access: The process of verifying a user’s or system’s identity in order to gain access to cloud resources is called authentication. On the other hand, access control deals with defining which people or systems are authorized to access specific data and what kinds of activities they can undertake. In cloud computing, ensuring that only authorized users or systems access sensitive data is crucial, and this requires implementing strong authentication protocols, such as multi-factor authentication (MFA). To prevent unwanted access, access control policies must be carefully drafted and regularly reviewed. Ensuring the security of cloud systems and preventing potential breaches requires a careful approach to authentication and access control.
2. Encryption of Data: Data encryption is a fundamental component of cloud data security. Data must be converted into a secure format throughout this procedure so that it can only be decoded with the matching decryption key. Cloud service providers frequently offer encryption options for data in transit, or information sent between the user and the cloud, as well as data at rest, or data that is stored. Encryption serves as a security measure, preventing unauthorized parties from decoding the data in case of interception or theft. Organizations can strengthen data protection, guarantee confidentiality, and combat potential breaches by implementing encryption techniques.
3. Backing Up and Recovering Data: Numerous things, including cyberattacks, human mistakes, and device malfunctions, can result in data loss. Cloud computing provides a dependable option for data backup and recovery. Strong backup plans that include frequent, safely stored backups in many locations are critical for enterprises. This proactive strategy enables swift data restoration, reducing downtime, and minimizing disruptions to business operations. Resilient backup strategies implemented in the cloud improve data loss prevention capabilities and support overall business resilience.
4. Monitoring Security and Detecting Threats: The risk landscape can quickly shift in dynamic cloud settings. To quickly recognize and address possible security issues, real-time security monitoring and threat detection systems must be put in place. Cloud service providers usually offer security tools and services that help businesses identify and mitigate risks more successfully. An organization’s ability to protect its cloud assets can be greatly increased by implementing threat intelligence feeds and making use of these technologies. Businesses may strengthen their entire cybersecurity posture and quickly respond to emerging threats in the dynamic cloud environment by being alert through real-time monitoring and utilizing available security tools.
5. Control and Compliance: One of the most important aspects of cloud data security is making sure that best practices and industry requirements are followed. Businesses must be aware of the specific compliance standards that apply to their sector and region. Cloud service providers facilitate the fulfillment of regulatory requirements by regularly providing compliance certifications for their services. Moreover, sustaining constant data security over time requires putting strong governance measures in place that include security rules, procedures, and frequent audits. Through proactive management of compliance requirements and the implementation of robust governance protocols, enterprises may reinforce cloud data security and exhibit a dedication to industry best practices and legal requirements for protecting confidential data.
NAVIGATING THE CLOUD SECURITY MAZE: ADDRESSING KEY CHALLENGES
As organizations facing cloud computing security challenges rely on cloud computing for its scalability, cost-effectiveness, and flexibility, they encounter a range of challenges when it comes to securing their data and infrastructure. This section explores the multifaceted landscape of cloud security challenges, delving into the complexities of managing security in cloud environments and addressing the shortage of skilled professionals. It also highlights the difficulties in maintaining compliance, staying ahead of evolving cyber threats, and seamlessly integrating cloud solutions with legacy systems.
Complexity of Cloud Environments: Managing security in complex cloud infrastructures with multiple services, providers, and configurations can be challenging.
Lack of Visibility: Organizations may struggle to gain complete visibility into their cloud environments, making it difficult to monitor and secure all assets effectively.
Security Skills Gap: There might be a shortage of skilled professionals with expertise in cloud security, which can hinder an organization’s ability to implement robust security measures.
Compliance and Legal Challenges: Meeting compliance requirements in the cloud, especially when dealing with data sovereignty and cross-border data transfer issues, can be complex and costly.
Constantly Evolving Threat Landscape: Cyber threats are continuously evolving, requiring organizations to adapt and update their security measures to stay ahead of attackers.
Integration with Legacy Systems: Integrating cloud solutions with existing legacy systems can introduce security challenges, as it may create potential vulnerabilities.
FAQ
What is cloud data security?
Cloud data security refers to the practice of protecting data that is stored, processed, and transmitted within cloud environments. It involves measures to ensure confidentiality, integrity, and availability while preventing unauthorized access and data breaches.
What are the key aspects of data security in the cloud?
The key aspects of data security in the cloud include confidentiality (protecting data from unauthorized access), integrity (ensuring data remains accurate and trustworthy), availability (ensuring uninterrupted access), authentication and authorization, and data lifecycle management.
What are some common cloud computing security issues?
Common cloud computing security issues include data breaches, data loss incidents, compliance challenges, and risks associated with inadequate access controls, shared infrastructure in multi-tenant environments, and third-party vulnerabilities.
Can you provide examples of real-world incidents related to cloud security?
Yes, examples include the 2019 Capital One data breach, the 2020 Microsoft data loss incident, the 2014 iCloud celebrity photo hack, the 2017 AWS S3 data breach, and the 2020 SolarWinds supply chain attack, among others.
What are some crucial measures for cloud data protection?
Important measures for cloud data protection include data encryption (both in transit and at rest), access control and identity management, regular auditing and monitoring, backup and disaster recovery strategies, and compliance and governance practices.

SUBBAIAH KU
Subbaiah Ku is the Regional Director for CertPro in Oman, bringing a wealth of expertise in process and system auditing. As a seasoned lead assessor, Subbaiah is dedicated to ensuring the highest standards in compliance and security. His unique blend of technical acumen, rooted in Mechanical Engineering, is complemented by a diverse range of certifications and extensive training.
HOW DOES THE NIST CYBERSECURITY FRAMEWORK FUNCTION, AND WHY IS IT IMPORTANT?
Emerging cyber threats make cybersecurity an essential consideration for organizations handling and managing data. In this regard, the NIST cybersecurity framework applies to improving your cybersecurity program. It is a set of guidelines that helps improve your...
UNDERSTANDING ISO 42001: A GUIDE FOR RESPONSIBLE AI MANAGEMENT SYSTEMS
The invention of artificial intelligence (AI) has changed the operational processes of many industries. However, the rapid growth of technology increases ethical, security, and privacy-related concerns. Therefore, the International Organization for Standardization...
EUROPEAN UNION’S ARTIFICIAL INTELLIGENCE ACT: HOW THIS GROUNDBREAKING LAW AFFECTS YOUR BUSINESS
Nowadays, Artificial Intelligence (AI) is transforming our lives exceptionally well. AI is now streamlining healthcare services, providing virtual assistance, and fulfilling queries. Technologies have boons and curses. Similarly, AI creates many concerns about...




