In today’s digitally interconnected society, the importance of privacy has surged to the forefront of discussions about ethics, technology, and personal rights. With the constant evolution of information technology, the boundaries between public and private spheres have become increasingly blurred, making the protection of privacy more vital than ever before.
Cyberattacks, data breaches, and unauthorized data exploitation have become pervasive threats, jeopardizing sensitive information ranging from financial records to personal conversations. Governments, Corporations, and Advertisers can amass substantial insights into individuals’ behaviors, preferences, and even thoughts, enabling the manipulation of decision-making processes and potentially curbing personal freedoms.
Preserving data privacy is essential for safeguarding human dignity, personal autonomy, and democratic values. It empowers individuals to express opinions, explore new ideas, and engage in activities without the fear of undue scrutiny. This article delves into the importance of privacy’s multifaceted dimensions, increasing digitalization, its impact on interferences with privacy, and how different standards help to protect data privacy in the digital age.
THE GROWING TREND OF DIGITALIZATION
The rapid rise of technology and the internet has revolutionized the way we communicate, access information, and conduct various aspects of our daily lives. One of the most significant impacts has been the proliferation of social media and online platforms, which have altered the dynamics of privacy. While these platforms offer unprecedented connectivity, they have also raised concerns about the erosion of personal privacy.
Data breaches and cybercrimes further exemplify the risks associated with technology and the internet. Major corporations and organizations have fallen victim to cyberattacks that compromise sensitive user information. The 2013 Yahoo breach exposed over three billion user accounts, while the Equifax breach in 2017 compromised the personal data of nearly 147 million people. These breaches highlight the vulnerability of personal data stored online and the potential for identity theft, financial fraud, and other malicious activities.
Cybercrimes involving ransomware attacks have also emerged as a significant threat. In these attacks, hackers gain unauthorized access to computer systems, encrypt data, and demand a ransom for its release. To address these challenges, governments and regulatory bodies worldwide are grappling with the formulation of comprehensive data protection and privacy regulations. The European Union’s General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) and California’s Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA) are examples of efforts to enhance user privacy rights and control over personal data.
In conclusion, the rise of technology and the internet has brought unprecedented benefits but has also raised concerns regarding the impact of social media on privacy and the susceptibility to data breaches and cybercrimes.
IMPACT OF INFERENCES WITH PRIVACY
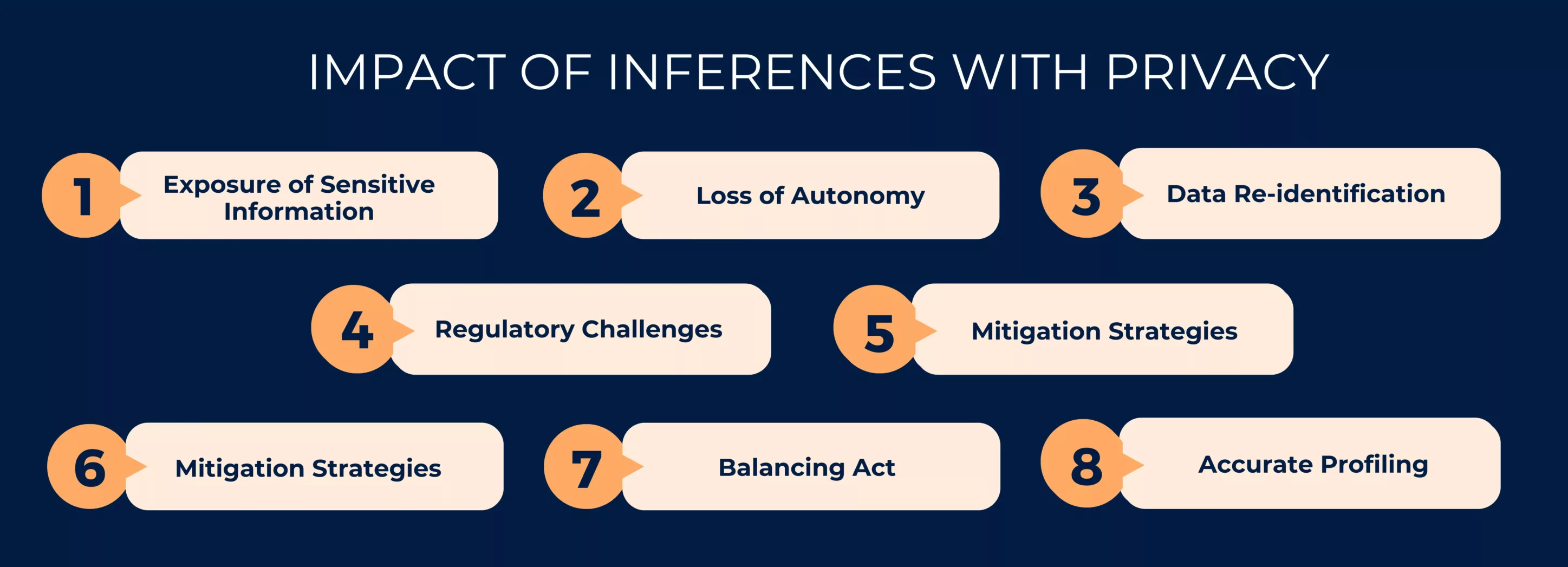
The impact of inferences on privacy is a complex and multifaceted issue that arises from the growing capacity of technology to glean detailed information about individuals from seemingly innocuous data.
The key impacts of inferences on privacy are:
1. Exposure of Sensitive Information: Inferences can reveal personal attributes, beliefs, and behaviors that individuals did not explicitly share, leading to potential privacy breaches.
2. Loss of Autonomy: Knowledge that actions are being analyzed and inferred can lead individuals to alter their behavior, reducing their freedom of expression and diversity of choices.
3. Data Re-identification: Even anonymized data used for inferences can sometimes be re-identified, compromising the promise of privacy protection.
4. Regulatory Challenges: Policymakers face the challenge of keeping pace with rapidly advancing technology to establish effective regulations that balance innovation and privacy protection.
5. Mitigation Strategies: Implementing advanced anonymization techniques, improving algorithmic transparency, and enhancing individual awareness are essential in mitigating the negative impacts of inferences on privacy.
6. Educational Efforts: Promoting data literacy among individuals can empower them to understand the implications of their digital footprint and make informed choices regarding data sharing.
7. Balancing Act: Striking a balance between deriving useful insights from data and safeguarding individual privacy requires collaboration between technology developers, policymakers, and society as a whole.
8. Accurate Profiling: Aggregating various data points through inferences can create highly accurate profiles, leaving individuals vulnerable to targeted marketing, manipulation, and potential discrimination.
In conclusion, while inferences driven by technology can offer valuable insights, their impact on privacy cannot be understated. Striking a balance between deriving useful information and safeguarding individual privacy is a complex challenge that requires collaboration between policymakers, technologists, and individuals themselves.
STANDARDS FOR PRIVACY
There are several privacy standards and frameworks that focus on the importance of privacy and data protection. These standards provide guidelines and best practices for organizations to ensure the privacy and security of individuals’ personal data.
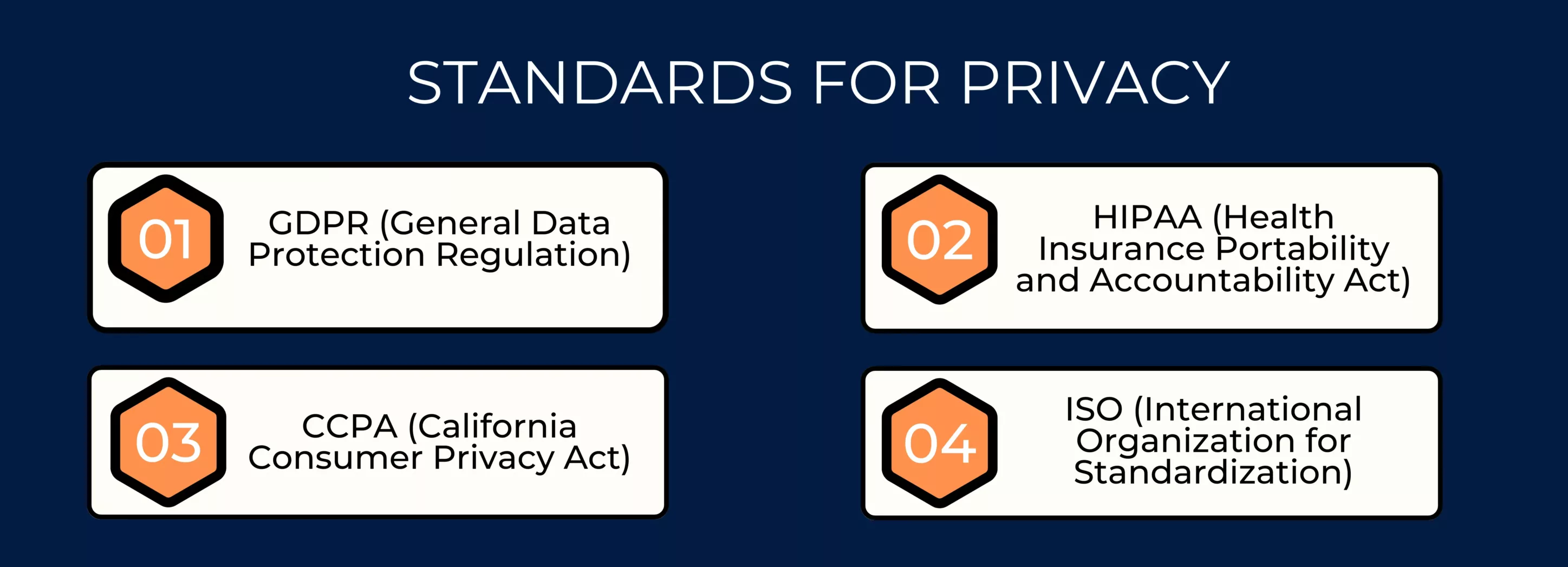
Each of them stands for, and their significance is:
1. GDPR (General Data Protection Regulation): The European Union (EU) introduced the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) in May 2018 as a comprehensive data protection law. It aims to strengthen and unify data protection regulations for individuals within the EU while addressing the export of personal data outside the EU.
2. HIPAA (Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act): HIPAA is a federal law in the United States enacted in 1996 that focuses on safeguarding sensitive patient health information. It is applicable to healthcare providers, health plans, and clearinghouses, as well as their business associates. HIPAA specifies privacy and security rules for protected health information (PHI).
3. CCPA (California Consumer Privacy Act): The California Consumer Privacy Act is a privacy law in the state of California, USA, enacted in 2018 and effective in 2020. The CCPA grants California residents the right to know what personal information businesses collect about them, the right to opt out of the sale of their personal information, and the right to request the deletion of their data.
4. ISO (International Organization for Standardization): ISO is an international standard-setting body that develops and publishes standards across various industries. In the context of data protection and information security, ISO has developed standards such as ISO/IEC 27001 and ISO/IEC 27701.
These regulations and privacy standards play a crucial role in shaping how organizations handle personal data, ensure the privacy of data, and maintain information security. They help establish guidelines, best practices, and legal requirements to protect individuals’ rights and data in an increasingly digital and interconnected world.
HOW DO THESE STANDARDS HELP WITH DATA PRIVACY?
GDPR, CCPA, HIPAA, and ISO are key regulations and privacy standards that play a crucial role in safeguarding the privacy of data and assuring the safekeeping of personal information Here’s how each of these contributes to data security:
1. GDPR (General Data Protection Regulation):
- Enhanced Individual Rights: GDPR grants individuals greater control over their personal data. It empowers them with rights such as the right to access their data and the right to be forgotten.
- Consent and Transparency: GDPR mandates organizations to obtain clear and explicit consent from individuals before collecting and processing their data.
2. CCPA (California Consumer Privacy Act):
- Consumer Rights: CCPA provides California residents with the right to know what personal information businesses collect about them and the right to opt out of the sale of their data.
- Increased Accountability: CCPA mandates businesses to implement data protection measures and maintain accurate records of data processing activities, enhancing their accountability for data security.
3. HIPAA (Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act):
- Health Data Protection: HIPAA establishes safeguards for the protection of sensitive health information, ensuring that patients’ medical records and health data remain confidential and secure.
- Administrative, Physical, and Technical Safeguards: HIPAA outlines security requirements for healthcare entities, including administrative policies, physical security measures, and technical safeguards such as encryption and access controls.
4. ISO (International Organization for Standardization):
- Information Security Management: ISO/IEC 27001 provides a systematic approach to managing information security risks, including those related to data security.
- Privacy Management: ISO/IEC 27701 extends ISO/IEC 27001 to cover privacy management, helping organizations implement measures to protect personal data and comply with privacy regulations.
Collectively, these regulations and standards promote responsible data handling, transparency, accountability, and individual rights, creating a framework that organizations can follow to ensure the privacy of data and maintain public trust.
SECURING THE FUTURE: EMBRACING DATA PRIVACY WITH CERTPRO
In the ever-evolving digital era, where personal information is both a valuable asset and a potential vulnerability, the significance of data privacy cannot be overstated. Fortunately, regulations and privacy standards like GDPR, CCPA, HIPAA, and ISO provide crucial pillars of support in safeguarding individuals’ rights and maintaining the integrity of personal data. CertPro emerges as a beacon of assurance. With its comprehensive expertise in data protection, CertPro offers a holistic approach to the importance of privacy and data management. Through meticulous audits, advanced security protocols, and proactive risk assessment, CertPro empowers businesses to instill trust in their clients, stakeholders, and partners. By partnering with CertPro, organizations not only navigate the complex terrain of data security but also showcase their commitment to ethical data practices.
FAQ
WHAT IS THE IMPORTANCE OF PRIVACY IN TODAY'S WORLD?
In the digital age, personal data is constantly shared and stored. Privacy ensures protection from cyber threats, unauthorized access, and unwanted surveillance.
HOW DOES TECHNOLOGY IMPACT PRIVACY?
Technology advances have blurred the lines between public and private spaces, necessitating robust privacy measures to safeguard personal information.
WHAT RISKS DOES A LACK OF PRIVACY POSE?
Without privacy, sensitive data can be exploited for fraud, manipulation, and identity theft, compromising individuals’ security and autonomy.
HOW DO REGULATIONS LIKE GDPR AND CCPA HELP WITH DATA SECURTIY?
Regulations empower individuals with control over their data and set standards for organizations, reinforcing the importance of privacy.
HOW DOES PRIVACY EMPOWER INDIVIDUALS?
Privacy allows for free expression, idea exploration, and other activities without undue scrutiny, preserving human dignity and democratic values.

About the Author
MOHAMMAD YASIN
Mohammad Yasin, Regional Manager in Jordan, is a cybersecurity specialist. With a dedicated focus on securing digital landscapes, he brings extensive experience in compliance and strategic cybersecurity measures to the forefront.
HOW DOES THE NIST CYBERSECURITY FRAMEWORK FUNCTION, AND WHY IS IT IMPORTANT?
Emerging cyber threats make cybersecurity an essential consideration for organizations handling and managing data. In this regard, the NIST cybersecurity framework applies to improving your cybersecurity program. It is a set of guidelines that helps improve your...
UNDERSTANDING ISO 42001: A GUIDE FOR RESPONSIBLE AI MANAGEMENT SYSTEMS
The invention of artificial intelligence (AI) has changed the operational processes of many industries. However, the rapid growth of technology increases ethical, security, and privacy-related concerns. Therefore, the International Organization for Standardization...
EUROPEAN UNION’S ARTIFICIAL INTELLIGENCE ACT: HOW THIS GROUNDBREAKING LAW AFFECTS YOUR BUSINESS
Nowadays, Artificial Intelligence (AI) is transforming our lives exceptionally well. AI is now streamlining healthcare services, providing virtual assistance, and fulfilling queries. Technologies have boons and curses. Similarly, AI creates many concerns about...