An objective third-party auditor performs the Service Organization Control 2 audit, which provides insightful data on the effectiveness of the organization’s controls and indicates to clients, stakeholders, and regulatory bodies that data protection is of the utmost importance.
This article aims to explore the various aspects affecting the timeline of a service organization control audit and provide a comprehensive understanding of how long the process typically takes.
WHAT IS THE SOC 2 AUDIT?
Service organization control 2 is a method for assessing service providers to ensure that they securely manage your data for the benefit of your company’s interests and the privacy of its clients. SOC 2 Security audit-conscious businesses must opt for a SaaS provider that has SOC 2 accreditation. Audits conducted under the TSOC (System and Organization Controls, formerly Service Organization Controls) framework provide an unbiased evaluation of the risks related to working with service providers and other third parties. They are crucial to risk management, internal governance, vendor management programs, and regulatory supervision. Service Organization Control 2 reports are unique to each organization, unlike PCI DSS, which has very strict criteria. Each one develops its own controls to adhere to one or more of the trust principles in accordance with its business operations. External auditors certify SOC 2 systems. Using the systems and processes in place, they evaluate how closely a vendor adheres to one or more of the five trust principles.
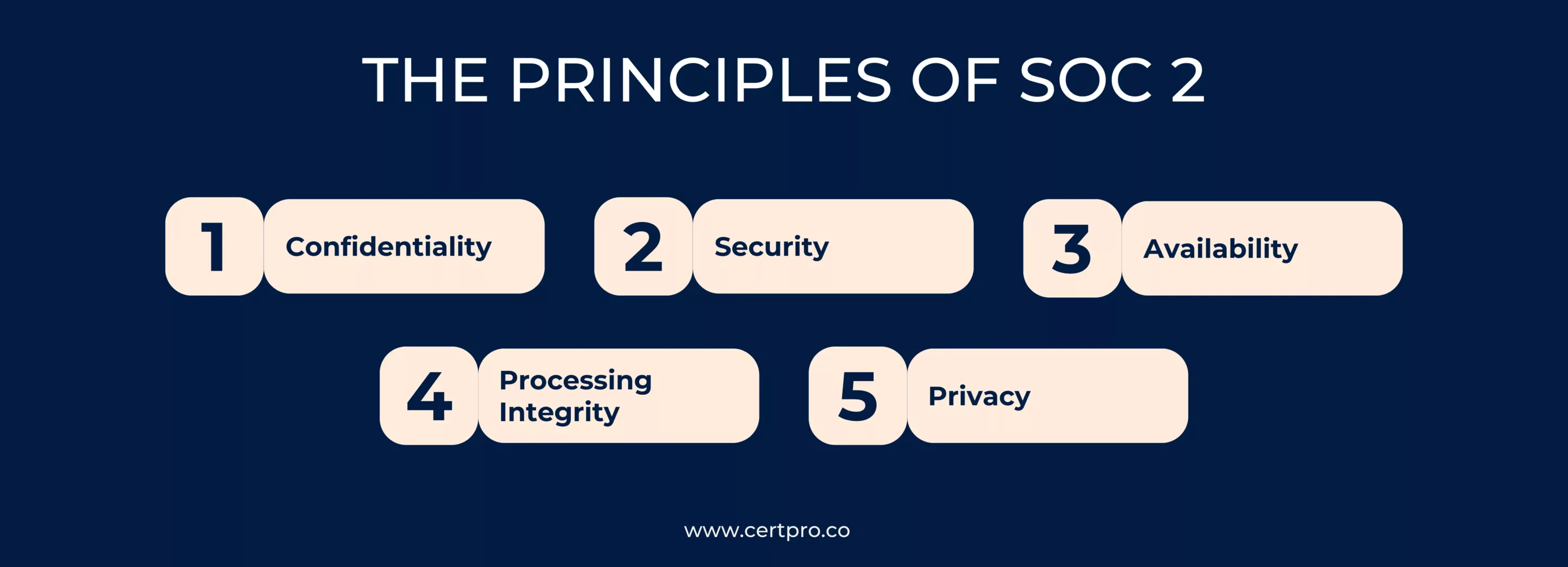
The five principles are:
- Confidentiality:If only a specific group of people or organizations are allowed access to and publication of the data, then it is deemed confidential.
- Security: SOC 2 security audit concept deals with preventing unwanted access to system resources.
- Availability: According to a contract or service level agreement, the accessibility of the system, goods, or services is referred to as the availability principle.
- Processing Integrity: In order to deliver the right data at the right price at the right time, a system must adhere to the processing integrity principle.
- Privacy: The privacy principle focuses on how the system gathers, utilizes, keeps, discloses, and discards personal data in compliance with the company’s privacy notice and guidelines described in the AICPA’s generally accepted accounting principles.
THINGS TO CONSIDER DURING A SOC 2 AUDIT
There is no universally applicable answer to the question of how long the SOC 2 audit procedure will take. Depending on your organization’s demands and other factors, the completion time may change.
Here are three factors to think about:
1. SOC 2 Audit and Report Type:The first variable that can affect the timeline is the sort of audit you decide to conduct.
- SOC 2 Type I: This is an examination of a corporation by an auditor at a particular moment in time that simply considers whether controls are properly designed.
- SOC 2 Type II: This evaluates how well a company’s controls perform over a predetermined time period, often three to twelve months.
2. Organizational Size and Complexity: How many employees and locations your company has will indicate how big it is. The auditor must assess additional systems as the firm grows, which might take more time and effort. As you start the audit process, bear this in mind.
3. Needs for Security: Strong security postures are crucial, but they might differ between businesses and sectors. An organization handling sensitive financial information, for instance, might have more protocols and tougher SOC 2 security audit regulations in place to safeguard its data. The time it takes to finish a SOC 2 audit can increase due to these security requirements and systems.
SOC 2 AUDIT PROCESS
Although every business is different and every audit is different, the SOC 2 audit process does adhere to a standard set of steps.
An overview of the SOC 2 audit process:
1. Determine Scope and Objectives: The service organization and the audit firm collaborate to define the scope and objectives of the audit.
2. Pre-Assessment Preparation: The service organization prepares for the audit by reviewing its internal controls and processes against the chosen SOC 2 criteria.
3. Engagement Letter and Planning: The audit firm and the service organization formalize their agreement through an engagement letter.
4. Fieldwork: The auditor performs on-site or remote testing of the controls and processes.
5. Testing: The auditor evaluates the design and operating effectiveness of the controls based on the defined criteria.
6. Sampling: Due to the potentially extensive nature of controls, auditors often use sampling techniques to assess a representative subset of controls and transactions.
7. Assessment of Control Effectiveness: The auditor assesses whether the controls are operating effectively throughout the audit period.
8. Reporting: Once the audit is complete, the auditor provides a detailed report that includes the following components:
- Type I Report:Describes the design of controls as of a specific point in time.
- Type II Report: Covers the design and operational effectiveness of controls over a specified period (usually six to twelve months).
9. Remediation and Follow-Up: If any control deficiencies are identified, the service organization takes corrective actions to address these issues.
10. Distribution of Report: The service organization can distribute the SOC 2 report to its customers, partners, and stakeholders to demonstrate its commitment to SOC 2 security audit and compliance.
It’s important to note that it may vary based on factors such as the audit firm’s approach, the specific criteria being assessed, and the complexity of the service organization’s operations.
TIMELINE OF SOC 2 AUDIT
The timeline for an audit of service organization control can vary depending on several factors, including the complexity of the organization’s systems and processes, the readiness of the organization for the audit, the availability of audit resources, and the specific requirements of the audit engagement.
A general timeline that provides an overview of the process of auditing SOC 2.
1. Preparation Phase (1-3 months prior to the start of the audit):
- Engage with an audit firm and define the scope and objectives of the audit.
- Develop a project plan and timeline for the audit, including key milestones and responsibilities.
2. Engagement and Planning (1-2 months prior to the start of the audit):
- Formalize the engagement with an engagement letter or contract.
- The audit firm develops a detailed audit plan, outlining testing procedures, sampling methods, and timelines.
3. Fieldwork and Testing (1-3 months, depending on scope):
- An auditor performs on-site or remote testing of controls and processes.
- Gather evidence, review documentation, and conduct interviews with key personnel.
- Assess the design and operating effectiveness of controls.
4. Assessment and Reporting (1-2 months, depending on complexity):
- The auditor evaluates control effectiveness and identifies any deficiencies.
- The auditor prepares the SOC 2 report, which includes the Type I or Type II report components.
5. Remediation and Follow-Up (1-2 months, if needed):
- The organization addresses and remediates control deficiencies.
- Auditors may conduct follow-up procedures to verify the effectiveness of remediation efforts.
6. Finalization and Distribution (1-2 weeks):
- The auditor finalizes the Service Organization Control 2 report based on the assessment and remediation efforts.
- The report is distributed to relevant stakeholders, such as customers and partners.
It’s important to note that this timeline is a general guideline and can vary based on the specific circumstances of each audit. Some organizations may require more time for preparation and remediation, especially if significant control deficiencies are identified.
STRATEGIES TO EXPEDITE THE SOC 2 AUDIT PROCESS
There are several strategies you can consider to streamline the process and help it progress more efficiently:
1. Thorough Preparation: Organizations can proactively prepare for the audit by conducting internal assessments, addressing control gaps, and ensuring comprehensive documentation of controls and processes.
2. Engage Early: Engaging with the audit firm well in advance and discussing expectations, timelines, and scope can help align both parties and reduce delays.
3. Clear Communication: Open and transparent communication with auditors during the audit process is essential. Timely responses to inquiries and requests for information can prevent bottlenecks.
4. Technology Adoption: Utilizing audit management software and secure document sharing platforms can streamline information exchange and document submission, reducing administrative overhead.
5. Mock Audits: Conducting mock audits or readiness assessments can identify potential issues and allow organizations to address them before the official audit, saving time during the actual assessment.
Choose experienced auditors who are well-versed in these requirements to guide you efficiently. Remember, while expediting is crucial, upholding accuracy and quality remains paramount. By combining these strategies, you can navigate the process swiftly while ensuring compliance and maintaining a comprehensive assessment.

ELEVATING DATA SECURITY THROUGH SOC 2 AUDITS WITH CERTPRO
FAQ
HOW LONG DOES A SERVICE ORGANIZATION CONTROL 2 AUDIT TYPICALLY TAKE?
WHAT FACTORS INFLUENCE THE TIMELINE OF A SERVICE ORGANIZATION CONTROL 2 AUDIT?
DOES THE SIZE OF MY ORGANIZATION AFFECT THE AUDIT DURATION?
ARE THERE DIFFERENT TIMEFRAMES FOR TYPE I AND TYPE II AUDITS?
CAN A SERVICE ORGANIZATIONS CONTROL 2 AUDIT BE EXPEDITED?

About the Author
ANUPAM SAHA
Anupam Saha, an accomplished Audit Team Leader, possesses expertise in implementing and managing standards across diverse domains. Serving as an ISO 27001 Lead Auditor, Anupam spearheads the establishment and optimization of robust information security frameworks.
HOW CAN STARTUPS ATTAIN SOC 2 COMPLIANCE IN 2024?
Trust is crucial for startups to do well in today's digital world. It's vital for establishing credibility with clients, especially in a data-driven environment where privacy is the main component. Therefore, getting a SOC 2 compliance report is crucial to building...
SOC TOOLS: How They Impact On Security Aspect Of The Organization
The changing cybersecurity landscape increases the importance of Security Operations Center (SOC) tools. Hence, it is essential for strengthening digital defenses and protecting against cyberattacks. SOC tools help security teams detect, monitor, and prevent security...
WHAT IS SOC FOR CYBERSECURITY?
In today's fast-paced digital landscape, ensuring robust cybersecurity measures is imperative for organizations aiming to protect sensitive data and maintain stakeholder trust. The American Institute of CPAs (AICPA) crafted the SOC for cybersecurity reporting...




