Artificial Intelligence continues to grow and become more relevant in workplaces. Customers widely use it to handle market products. Organizations are desperately using AI for their businesses, ensuring that the AI systems comply with the new rules and regulations. In addition, AI compliance regulation is a complex and changing process. Therefore, organizations must stay updated regarding AI security. Hence, an effective AI security solution offers sustainable solutions for managing and developing responsible AI systems. Regulatory compliance ensures AI security. Consequently, AI compliance confirms that AI systems comply with laws and regulations. It scrutinizes an organization’s AI-based systems to ensure they follow AI regulations. Consequently, the ethical use of data to train AI systems confirms that AI-based systems are free from discrimination.
Hence, the regulations and compliance guarantee that AI systems are safe and that no one can use them to invade privacy. The regulatory complaint confirms that AI systems are utilized responsibly to benefit society. This article discusses the risks and threats associated with AI security and explains the coping mechanisms. You must read the whole article to clarify doubts about AI security risks.
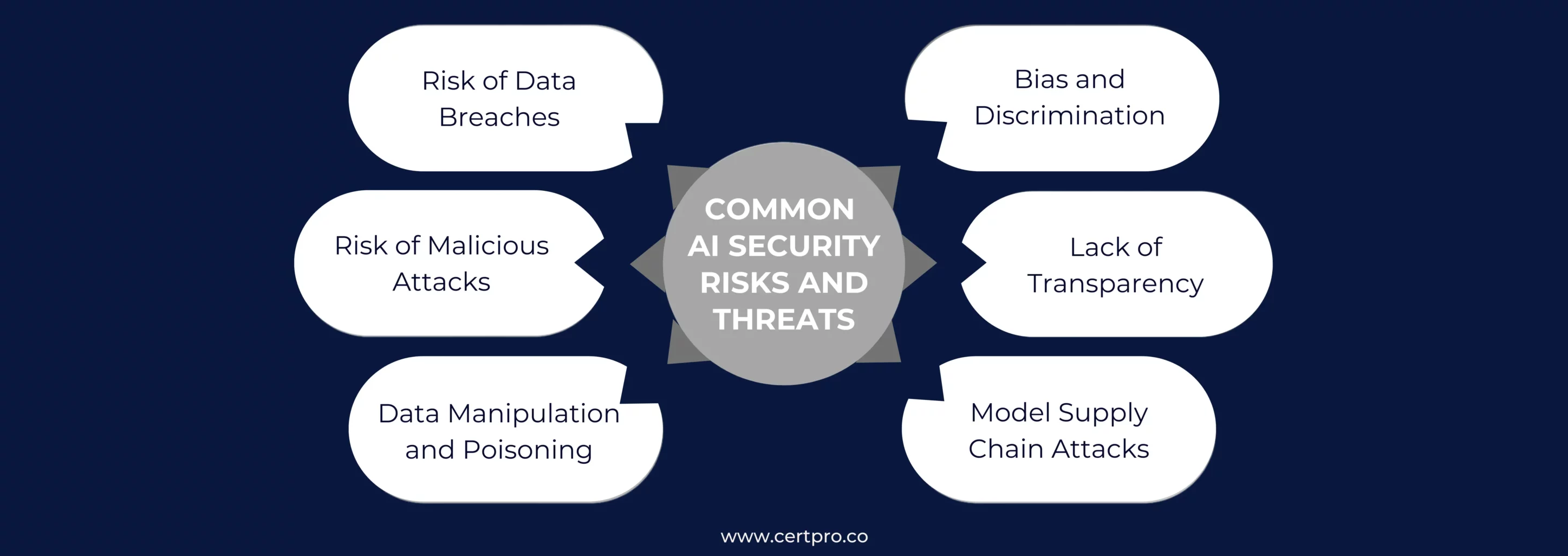
COMMON AI SECURITY RISKS AND THREATS
AI has the potential to change the landscape of many industries. It can help different sectors maintain cybersecurity. Below is a list of the security risks associated with AI.
Risk of Data Breaches:AI models handle large volumes of data, including labeled instances of different events. In this regard, if an AI system identifies threats in network traffic, then the system must have data relevant to regular instances and malicious traffic. Therefore, the standard training data can contain sensitive customer and business information. Hence, storing sensitive data to train the AI can cause data breaches.
Risk of Malicious Attacks: AI systems are trained to differentiate benign files from potential malware in network traffic. Similarly, hackers can train their AI systems to identify gaps in the security model and manipulate the stored data.
Data Manipulation and Poisoning: The data used to train AI models can be manipulated. Hackers can introduce new data that alters the exact trained data. The main aim is to train the AI model incorrectly to manipulate the data storage. Therefore, the system cannot recognize the malware if the training data has been manipulated.
Bias and Discrimination: AI systems are trained with input data, which enables them to build sophisticated systems that offer desired outputs. If the AI system gets biased training data, it produces biased systems. A typical example of a biased AI system is facial recognition. Thus, the systems are predominantly trained on images of people based on their specific facial expressions or demography. Therefore, the AI systems sometimes cannot recognize the faces if mild changes occur.
Lack of Transparency: AI systems can work based on specific patterns, trends, and relationships. The training sessions create data patterns for decision-making and identification processes. However, the assumed patterns of the AI systems can cause bias and discrimination. Thus, AI systems can face errors and transparency issues due to corrupted training data.
Model Supply Chain Attacks: AI system training is a complex process. The organization needs to manage vast amounts of data and label it to train AI systems. The process requires expert handling and techniques. Therefore, many organizations use AI models developed and taught by a third-party vendor. This puts the internal data at risk, and hackers can attack third-party vendors and manipulate the training data to produce corrupt AI models.
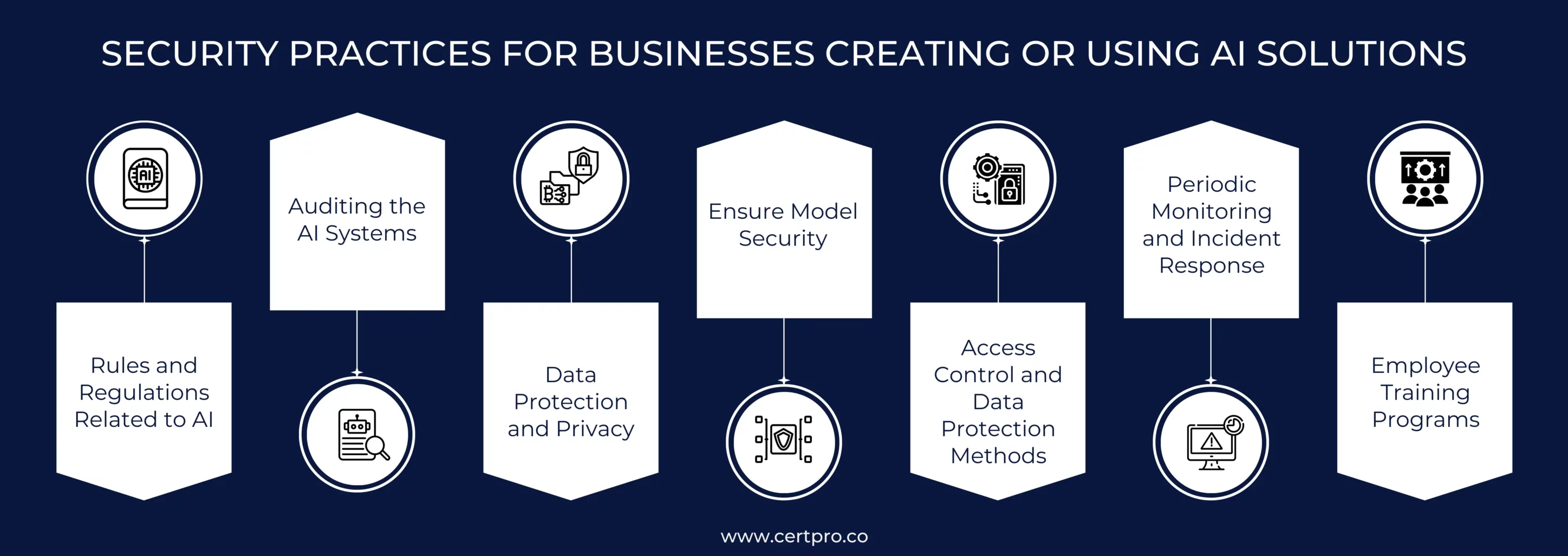
SECURITY PRACTICES FOR BUSINESSES CREATING OR USING AI SOLUTIONS
The following steps can help in implementing a practical AI system:
Step 1: Rules and Regulations Related to AI: The EU government is working towards implementing AI regulations in the form of the EU AI Act, which was introduced in 2021. The act restricts the use of AI in the EU for specific purposes and categorizes AI systems into three risk categories: unacceptable risk, high-risk applications, and unregulated risks. The act aims to eliminate the dangers of data violations and privacy with AI systems. It ensures AI security solutions for the betterment of society and individuals.
ISO/IEC 42001 is the first global certification process that ensures the responsible development and deployment of AI systems. It offers guidelines and structure for monitoring AI use, reducing the risk of data breaches. The certification process showcases that the organization follows strict AI use and deployment rules.
Step 2: Auditing the AI Systems: The periodic audit of AI systems avoids security and privacy-related risk issues. Therefore, the organization can seek help from an external auditor to perform the AI systems audit. The auditing process considers vulnerability assessments and system reviews. It encompasses data security and privacy. Thus, it reduces the risk of data manipulation and violation in AI-based technologies. In addition, it ensures compliance with the AI regulation and confirms AI security. Regular monitoring and auditing emphasize the responsible use of AI that benefits businesses and the community.
Step 3: Data Protection and Privacy: Organizations must implement robust data encryption and scrubbing techniques before using AI technologies. The main concern related to AI is protecting and maintaining data privacy and security. Therefore, a security program must be executed and audited regularly. In addition, vendor risk management is crucial in mitigating risks related to AI systems. Organizations must understand the types of data shared with AI solutions and how the business intends to use them.
Step 4: Ensure Model Security: Understanding the security posture of AI models and making wise decisions about which is best for your business is essential. Therefore, model validation and testing help identify potential susceptibilities. Consequently, the implementation of anomaly detection technology supports security measures. It helps identify unexpected deviations in AI models. Furthermore, AI applications require proactive error and exception management systems to minimize disruptions and potential security flaws. In the case of outsourcing AI models, code-signing mechanisms ensure integrity, authenticity, and AI security.
Step 5: Access Control and Data Protection Methods: Proper access control and data protection methods are necessary in a security program. Their importance increases severalfold when they relate to AI-based systems. Therefore, privileged access control and model repositories prevent model stealing. In addition, prompt input validation prevents injection attacks, and limiting queued actions precludes denial of service attacks. AI systems start considering the input patterns to conclude. This process of identification can make the online journey more manageable. Data protection is another concern related to AI systems. While a large data set produces more accurate results while training AI systems, it may increase the risk of data breaches. AI systems can de-anonymize personal data, which leads to data reidentification. Therefore, it indicates that AI reduces data breaches and privacy leakage risks. Thus, the organization must implement compliance to ensure data privacy.
Step 6: Periodic Monitoring and Incident Response: The organization should conduct periodic AI risk and threat assessment procedures to recognize and mitigate emerging risks within AI models. In this context, regular monitoring processes ensure the integrity of AI systems and reduce the risk of data manipulation. The organization must continue vulnerability scanning and monitoring resource utilization to recognize security threats related to AI. Therefore, the regular monitoring processes develop a proactive protocol for mitigating risks. Organizations should implement a robust incident response system that oversees AI responses. For example, detecting AI tools in the data processing and handling process required immediate action. Hackers can use AI tools to scan your organization’s AI-based systems. Hence, the identification of such incidents reduces AI threats.
Step 7: Employee Training Programs: Implementing regulatory compliance requires training programs to educate the team. These programs share information regarding the importance of security posture and relevant risks with AI usage. In addition, the training programs must include the organization’s policies and expectations regarding AI use. Furthermore, the team must have sufficient information regarding their actions in incident response. Therefore, implementing the AI security posture is beneficial and necessary for the organization. Thus, employee training fosters transparency and accountability in mitigating the potential risks of AI models and protecting the data.
FINAL THOUGHTS
In this article, we discuss the AI security-related risks and the measures that ensure trustworthy AI solutions for the organization. In addition, most AI security risks interfere with data security and quality. If the organization can train its AI systems safely, it will enable data security and accuracy. Nevertheless, lacking resources and expertise can make the process difficult, which risks the data. Therefore, the organization must incorporate regulatory compliance to ensure AI systems’ safety and security. However, non-compliance may result in high fines and penalties. Thus, the organization must implement a regulatory framework for managing the AI systems.
FAQ
What is the regulation of AI algorithms?
Controlling AI algorithms in diverse industries involves industry-specific standards, transparency requirements, and prohibitions for distinctive uses.
Can AI cause cyber attacks?
Yes, cyber hackers can use AI technologies to hack. However, this is a sophisticated and complex matter to detect and mitigate.
How to use AI in security?
AI improves security by improving threat detection, response capabilities, and overall cybersecurity measures. It has advanced threat detection and real-time monitoring capabilities that AI helps in threat detection.
Will AI replace cyber security?
AI can be a valuable part of cybersecurity, but inclusive solutions are needed. Thus, AI can augment, not replace, human expertise in cybersecurity.
Is generative AI a security risk?
The development of generative AI will affect cybersecurity. Cyberattackers are using generative AI.

About the Author
ANUPAM SAHA
Anupam Saha, an accomplished Audit Team Leader, possesses expertise in implementing and managing standards across diverse domains. Serving as an ISO 27001 Lead Auditor, Anupam spearheads the establishment and optimization of robust information security frameworks.
HOW DO GRC TOOLS HELP IDENTIFY AND MITIGATE RISKS?
In today’s fast-paced business environment, emerging threats and risks negatively influence business operations. Threats can arise from different sources, such as cybersecurity compliance requirements, supply chain disruption, and natural disasters. Thus, the...
HOW DOES THE NIST CYBERSECURITY FRAMEWORK FUNCTION, AND WHY IS IT IMPORTANT?
Emerging cyber threats make cybersecurity an essential consideration for organizations handling and managing data. In this regard, the NIST cybersecurity framework applies to improving your cybersecurity program. It is a set of guidelines that helps improve your...
UNDERSTANDING ISO 42001: A GUIDE FOR RESPONSIBLE AI MANAGEMENT SYSTEMS
The invention of artificial intelligence (AI) has changed the operational processes of many industries. However, the rapid growth of technology increases ethical, security, and privacy-related concerns. Therefore, the International Organization for Standardization...




