In an era characterized by unparalleled technological advancements and interconnectedness, the concept of privacy has taken on renewed significance. As the world embraced the digital revolution, concerns about the protection of personal information and data security emerged as paramount. In response, Global Privacy Standards have evolved to address these challenges, providing a framework to safeguard individual rights in an increasingly digitized landscape.
The dawn of the 21st century witnessed a surge in data breaches, identity theft, and intrusive surveillance practices. These developments prompted governments, international organizations, and the private sector to recognize the urgent need for cohesive privacy regulations. Initiatives like the European Union’s General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) and the California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA) marked the initial steps towards establishing a more robust privacy framework.
This article delves into the multifaceted evolution of International Privacy Standards, examining their historical roots, the driving forces behind their development, their benefits and challenges, and the transformative impact they have on societies, businesses, and governments worldwide.
WHAT ARE GLOBAL PRIVACY STANDARDS?
It refers to a set of universally accepted principles, Global Privacy Regulations, and guidelines aimed at safeguarding individuals’ personal information and privacy rights in an increasingly interconnected world. These standards provide a framework for data protection, transparency, and accountability, ensuring that individuals have control over their personal data and that organizations handle it responsibly.
These are essential for various reasons. They promote trust between individuals and organizations by assuring that personal data is handled responsibly. They facilitate international data transfers by creating a common ground for data protection practices, reducing legal and regulatory complexities. These standards also encourage businesses to adopt ethical data practices, fostering a culture of responsible data handling.
In many cases, governments or international bodies implement these standards as Global Privacy Laws and regulations. Notable examples include the European Union’s General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) and the Asia-Pacific Economic Cooperation (APEC) Privacy Framework. However, the core principles of International Privacy Standards often go beyond legal requirements, emphasizing ethical considerations and responsible behavior in the realm of data handling.
As technology evolves and continues to expand the ways in which data is collected and used, it assumes a vital role in protecting individual privacy rights, fostering digital trust, and ensuring that appropriate safeguards for personal data accompany the benefits of the digital age.
BENEFITS OF GLOBAL PRIVACY STANDARDS
It offers a wide array of benefits that extend to individuals, businesses, governments, and society at large. These benefits contribute to a more secure, transparent, and harmonious digital environment.
Some of the key advantages are:
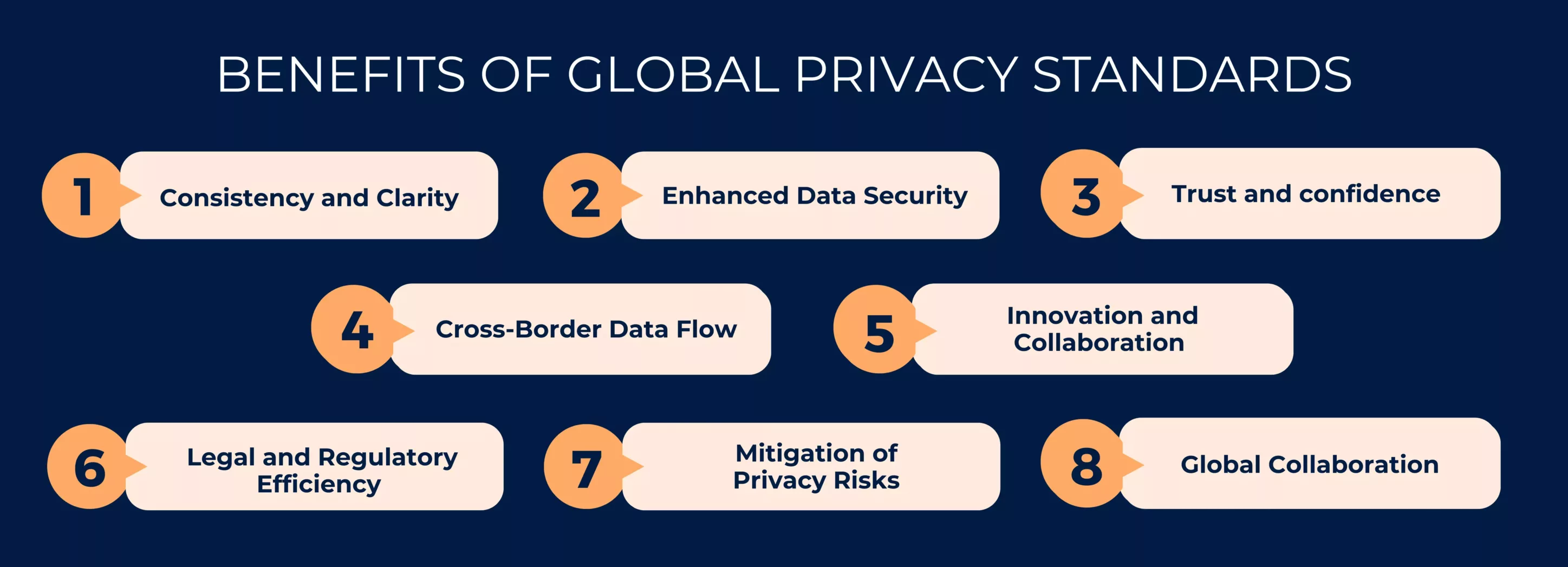
1. Consistency and Clarity: International privacy standards establish consistent and clear data protection frameworks for privacy across different countries and regions. This clarity helps individuals understand their rights and responsibilities, making it easier for them to navigate the digital landscape.
2. Enhanced Data Security: Adhering to this is what compels organizations to implement robust security measures to protect personal data.
3. Trust and confidence: They maintain trust between individuals and organizations. When people know their data is handled responsibly and transparently, they are more likely to engage with digital services.
4. Cross-Border Data Flow: Global standards facilitate the smooth transfer of data across international borders. This is particularly important for businesses that operate globally or rely on data from different regions.
5. Innovation and Collaboration: By providing a common baseline for data protection, it encourages innovation.
6. Legal and Regulatory Efficiency: For governments, global standards streamline the development and enforcement of Global Privacy Laws. This reduces legal complexity and enhances the ability to collaborate on global issues such as cybersecurity and cross-border data investigations.
7. Mitigation of Privacy Risks: The comprehensive nature of Global Standards helps mitigate risks associated with unauthorized data collection, profiling, and surveillance.
8. Global Collaboration: The establishment of Global standards encourages collaboration between countries and organizations. Governments, businesses, and Civil society can work together to address shared challenges and develop solutions that benefit everyone.
In conclusion, it offers a host of benefits that collectively contribute to a safer, more transparent, and more efficient digital environment.
PRIVACY STANDARDS WHICH ARE APPLICABLE GLOBALLY
Applying it globally is crucial to protecting individuals’ personal data and ensuring consistent data handling practices across different jurisdictions.
Several key global standards have gained widespread recognition and adoption:
1. General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR): The European Union enforces GDPR, which stands as one of the most influential global privacy regulations. It applies to organizations processing personal data of EU citizens, regardless of the organization’s location.
2. California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA): Focused on protecting Californian consumers’ privacy rights, CCPA grants individuals control over their personal data collected by businesses.
3. Personal Information Protection and Electronic Documents Act (PIPEDA): Canada’s privacy law applies to the private sector, governing how organizations collect, use, and disclose personal information.
4. ISO/IEC 27701: This privacy extension to ISO/IEC 27001 provides guidance for establishing and maintaining a Privacy Information Management System (PIMS). It helps organizations manage and protect personal data in line with various privacy regulations.
5. Brazilian General Data Protection Law (LGPD): Similar to GDPR, LGPD safeguards personal data in Brazil and has implications for organizations processing Brazilian citizens’ data.
6. Convention 108: The Council of Europe created this treaty with a focus on protecting individuals’ rights regarding the processing of personal data. It outlines common privacy principles and establishes mechanisms for international data transfers.
7. OECD Privacy Guidelines for Personal Data Flows: The Organization for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD) establishes these guidelines, providing a framework for safeguarding personal data in an era of globalization.
While these standards have a significant global impact, it’s essential to consider the specific legal requirements and nuances of each jurisdiction. Organizations operating across different regions should adapt their privacy practices to comply with the relevant standards and regulations applicable in those areas.
CHALLENGES FOR GLOBAL PRIVACY STANDARDS
The establishment and maintenance of international privacy standards face a range of intricate challenges that stem from the complex nature of data-driven economies, differing cultural norms, and the rapidly evolving technological landscape. These challenges pose significant hurdles to creating a unified framework that effectively protects individuals’ privacy rights on a global scale.
1. Cultural and Jurisdictional Diversity: One of the foremost challenges lies in reconciling the cultural and legal differences across various nations. Privacy expectations and practices vary widely across cultures, making it difficult to draft a one-size-fits-all standard that resonates universally.
2. Technological Advancements: The relentless pace of technological evolution introduces new complexities. Emerging technologies such as artificial intelligence, biometric identification, and blockchain are introducing novel privacy concerns that existing standards may not adequately address.
3. Cross-Border Data Flows: In an interconnected world, data flows seamlessly across borders. However, varying global privacy laws and data protection regulations can hinder these flows, leading to compliance difficulties for businesses operating globally.
4. Enforcement and Compliance: Even with robust standards in place, ensuring compliance remains a challenge. Different jurisdictions have varying levels of enforcement capacity, leading to inconsistencies in how privacy breaches are handled.
5. Emerging Privacy Issues: As technology advances, new privacy issues emerge. These include the ethical implications of AI decision-making, biometric data usage, and the integration of privacy considerations in emerging fields like quantum computing.
6. Public Awareness and Education: The success of global standards hinges on the awareness and understanding of individuals, organizations, and governments. Raising awareness about privacy rights, data breaches, and Responsible data handling practices is an ongoing challenge, requiring concerted efforts in education and outreach.
Addressing these challenges requires collaborative efforts between governments, international organizations, businesses, and civil society. Striving towards adaptable standards that can evolve with the changing landscape of technology.

NAVIGATING THE FUTURE OF GLOBAL PRIVACY STANDARDS
The evolution of International Privacy Standards stands as a crucial milestone in safeguarding individual rights and fostering a secure online environment. These standards have emerged as a response to the intricate challenges posed by data-driven economies and an interconnected world.
While navigating the complexities of diverse cultures, rapid technological shifts, and varying legal Data Protection frameworks, it offers a common foundation for responsible data handling. Overcoming these hurdles necessitates collaboration, adaptability, and continuous education. By embracing evolving technologies while adhering to ethical data practices, a harmonious balance can be achieved between innovation and privacy protection.
In conclusion, it represents a collective commitment to ensuring that the digital age progresses hand in hand with the values of privacy, security, and individual empowerment. As we move forward, these standards will play a pivotal role in shaping the future of privacy, underpinning a digital landscape where rights are upheld and individuals thrive in the evolving technological panorama.
FAQ
WHY ARE GLOBAL STANDARDS ESSENTIAL?
WHAT BENEFITS DOES GLOBAL PRIVACY OFFER?
HOW CAN CHALLENGES BE ADDRESSED?
WHY ARE GLOBAL STANDARDS SIGNIFICANT FOR THE FUTURE?
HOW CAN BUSINESSES PREPARE FOR GLOBAL STANDARDS?

About the Author
MOHAMMAD YASIN
Mohammad Yasin, Regional Manager in Jordan, is a cybersecurity specialist. With a dedicated focus on securing digital landscapes, he brings extensive experience in compliance and strategic cybersecurity measures to the forefront.
HOW DOES THE NIST CYBERSECURITY FRAMEWORK FUNCTION, AND WHY IS IT IMPORTANT?
Emerging cyber threats make cybersecurity an essential consideration for organizations handling and managing data. In this regard, the NIST cybersecurity framework applies to improving your cybersecurity program. It is a set of guidelines that helps improve your...
UNDERSTANDING ISO 42001: A GUIDE FOR RESPONSIBLE AI MANAGEMENT SYSTEMS
The invention of artificial intelligence (AI) has changed the operational processes of many industries. However, the rapid growth of technology increases ethical, security, and privacy-related concerns. Therefore, the International Organization for Standardization...
EUROPEAN UNION’S ARTIFICIAL INTELLIGENCE ACT: HOW THIS GROUNDBREAKING LAW AFFECTS YOUR BUSINESS
Nowadays, Artificial Intelligence (AI) is transforming our lives exceptionally well. AI is now streamlining healthcare services, providing virtual assistance, and fulfilling queries. Technologies have boons and curses. Similarly, AI creates many concerns about...




