Businesses are growing faster and with new technological advancements. Thus, streamlining the operation process is essential to keeping overhead costs low. Implementing an integrated management system provides a framework for eliminating redundancies in the process. Therefore, an integrated management system reduces duplications and improves the functionality. It is an effective measure compared to incorporating a separate management system. An Integrated Management System streamlines an organization’s multiple management systems. Nowadays, integrated management systems incorporate many management systems to improve their efficacy. The primary objective is to maximize resources and manage the operational process.
What is IMS, and how does it work for my organization? To learn the details, you need to delve into the article thoroughly. We will discuss the IMS process and prospect in detail. So, read the article to enrich your knowledge about IMS.
What is an Integrated Management System?
An integrated management system (IMS) is planned to integrate all management systems into one place. IMS transforms the organization’s management system into a singular unit that works toward an identical goal. In addition, the process improves productivity and efficiency within the organization. In the case of large companies, multiple units work together. Thus, the execution of an integrated management system ensures that all departments work together without any conflict. When organizations consolidate all information and work as a singular system, they can reduce overhead costs, improve productivity, and ensure uniform system controls.
IMS helps manage the organization’s operational process and streamline multiple management systems, such as quality, environment, and safety. For example, quality control and environmental management have many standard criteria. In addition, both are contributing to making the organization safe and efficient. Thus, IMS prevents duplicating processes and reduces unnecessary workload. It merges existing systems and implements the best practices per the organization’s needs.
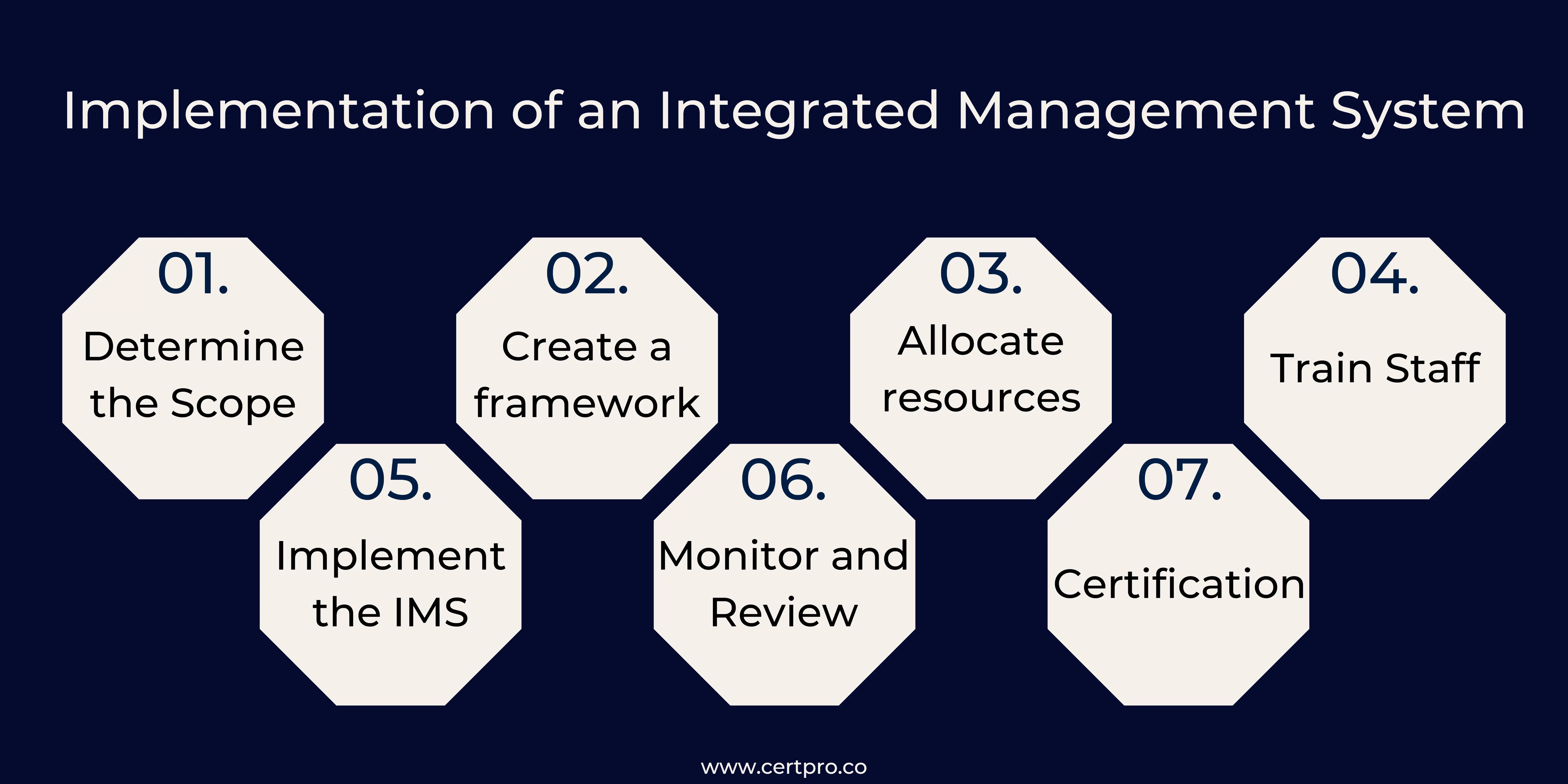
Implementation of an Integrated Management System
An effective IMS needs considerable key components to integrate various management regulations successfully. The implementation process might be complicated. However, the following steps can be followed for better results:
Scope Assessment: Gap analysis helps you recognize the current state of the organization’s management system and make wise decisions in the integration process.
IMS Framework Development: Create a unified framework and merge the relevant systems. This process will construct a consistent management system for your organization. The framework must combine all management systems into one. In addition, it develops rules and regulations to ensure that businesses achieve their goals and standards.
Employee Training: Train the employees on the IMS and the process. This will enable their understanding of the process and responsibilities.
Framework Implementation: Incorporate the IMS into the organization’s operation process.
Monitoring and Review: The process requires continuous monitoring and review. Identify areas for improvement and adjust them accordingly.
Certification Process: Achieve compliance certification from the concerned body and maintain the standards.
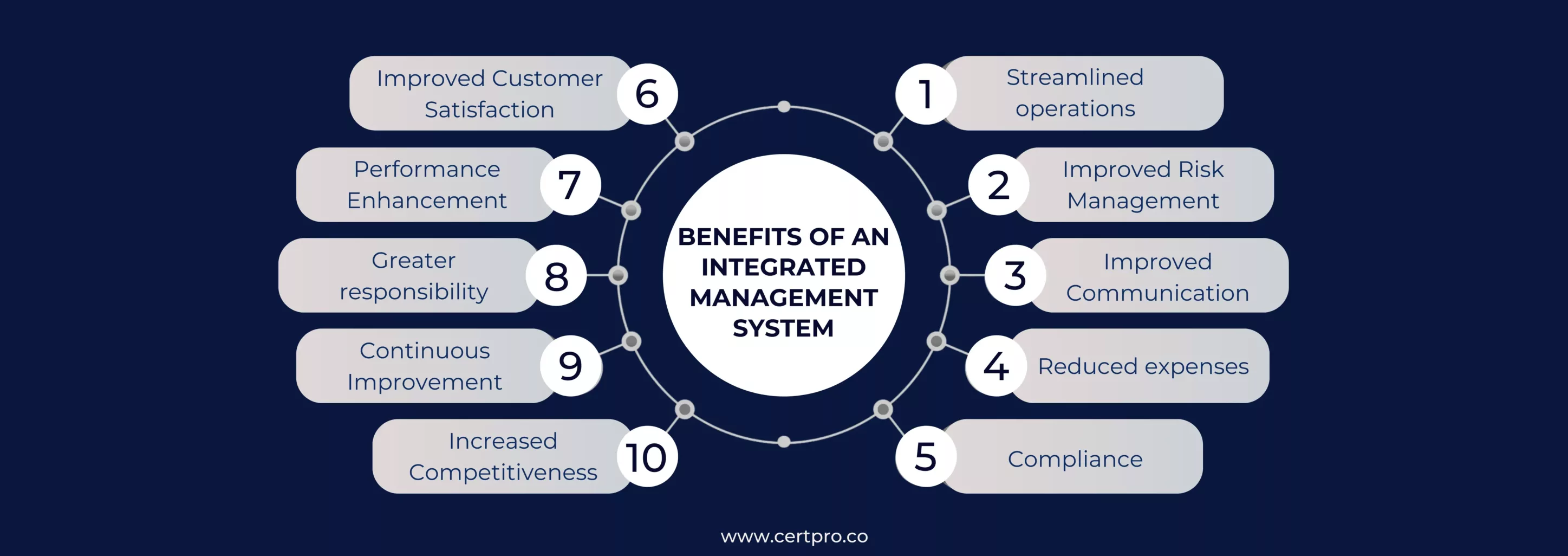
Benefits of an Integrated Management System
An integrated management system is a powerful tool that helps the organization achieve its goals efficiently. It combines multiple processes into a single one. The benefits of IMS are enormous, including streamlining the process and avoiding duplicate regulations. Some others are listed below:
Improving Performance: IMS has an optimistic impact on the specific components of the management system. It enhances the quality of services, increases productivity, ensures safety, and reduces risks.
Eliminating Redundancies: The most crucial benefit of IMS is that it is aligned with the standards needed to develop a single management system. It can be policies, procedures, or resources. The process enables a single training process, documentation, internal audits, reviews, and improvements. It saves money, time, and effort in maintaining multiple management systems.
Accountability: Integrate multiple management systems to establish cohesive objectives, resources, and procedures. Aligning with the system enhances accountability.
Establishing Consistency: An integrated approach creates consistent management systems. Therefore, incorporating IMS makes the systems less complicated and effortless to maintain. The standard set of objectives gets priority, and all work together to achieve the goal.
Reducing Bureaucracy: IMS helps reduce bureaucracy by eliminating redundancy. Multiple management standards can cause dilemmas in the decision-making process, causing different layers of hierarchy to interfere. Thus, the incorporation of an integrated management system creates a systematic approach. Developing process owners in IMS can help share responsibilities and accountabilities, eliminating the barrier in the decision-making process.
Cost Reduction: IMS allows your organization to conduct an audit and gap analysis. In addition, it is entitled to optimize processes and resources. Merging processes and compact auditing reduces the cost of maintenance and monitoring.
Optimize Processes and Resources: The integrated management process optimizes the operational process and modulates resource management. The process implementation prioritizes rather than implementing the additional system.
Reducing Maintenance: Ongoing compliances require continuous monitoring. Furthermore, an integrated management system streamlines the process, allowing organizations to focus on improvements.
Integrated Audits: An integrated management system demands an integrated audit process. It reduces the resources and costs related to the process.
Facilitating Decision Making: Eradicating unnecessary procedures and merging the system helps in understanding the exact position of the organization. Therefore, the management can make wise decisions for the betterment of the organization.
Annex SL and Integration
Annex SL consists of documents explaining the structure of the ISO management system. Hence, it was developed to streamline the current protocol and transform that existing management process into an IMS. In addition, the Annex Sl structure has been introduced in the latest ISO 9001 and 14001, making the standards more compatible and effective. Furthermore, another benefit of consolidation is the adoption of integrated management systems. It will now ease the transition into this model.
Popular Management System:
Organizations follow multiple management systems for ethical operations. Therefore, integrating all the systems and processes into one framework enables them to work as a single unit toward a unified goal.
- Environmental Management System: An EMS identifies continuous improvements in an organization’s environmental position and performance. It reduces environmental risk in workplaces.
- Food Safety Management System: It confirms that the food industry follows certain rules and guidelines to ensure product quality. Therefore, the regulations ensure customer safety and reduce food-related hazards.
- Information Security Management System: An information security management system ensures that the organization follows ethical rules and regulations in managing and handling data security. It reduces the risk of data breaches and strengthens the organization’s security.
- Energy Management System: An energy management system ensures that the organization improves its energy usage as it positively impacts the environment.
- Quality Management System: A QMS is a set of procedures and policies required for business planning and execution. It has a direct impact on customer satisfaction and business growth.
It is concluded that an organization must have an integrated management system that addresses the goal. A single business cannot manage multiple management systems in a single setting. Therefore, integrating standards created opportunities to improve the business objectives. Hence, an Integrated Management System may assist firms in achieving their goals and dominating a competitive market in the modern business environment, where efficiency, effectiveness, and sustainability are crucial. Thus, by embracing an IMS, organizations can ensure that they are well-positioned to meet the challenges and opportunities of the future.
FAQ
Is IMS suitable for small businesses?
Yes, a firm of any size may use an IMS. Implementing an IMS can help small businesses by streamlining operations, cutting costs, and increasing overall performance.
Does compliance with management system standards need an IMS?
The answer is no; adherence to management system standards does not require the use of an IMS. Implementing an IMS, however, can assist organizations in managing numerous systems more successfully and efficiently, lowering costs, and enhancing overall performance.
Is it possible for a company to integrate some management systems but not others?
Depending on its needs and goals, a business may decide to integrate some management systems but not others. However, there may be more advantages and efficiencies to be had by integrating all pertinent management systems.
What are integrated management systems' main objectives?
Organizations may detect and handle a wide range of system risks, including financial, strategic, competitive, security, safety, and environmental risks, using integrated management systems. All of this is done while ensuring ongoing organizational progress.
For an Integrated Management System, who is accountable?
The leadership team, the quality manager, the environment manager, and the health and safety officer have worked with the managing director to specify the resources required to build, implement, run, and enhance the integrated management system.

About the Author
RAGHURAM S
Raghuram S, Regional Manager in the United Kingdom, is a technical consulting expert with a focus on compliance and auditing. His profound understanding of technical landscapes contributes to innovative solutions that meet international standards.
AI SECURITY: UNDERSTANDING THREATS AND COMPLIANCE SOLUTIONS
Artificial Intelligence continues to grow and become more relevant in workplaces. Customers widely use it to handle and market products. Organizations are desperately using AI for their businesses and ensuring that the AI systems comply with the new rules and...
HOW DOES THE NIST CYBERSECURITY FRAMEWORK FUNCTION, AND WHY IS IT IMPORTANT?
Emerging cyber threats make cybersecurity an essential consideration for organizations handling and managing data. In this regard, the NIST cybersecurity framework applies to improving your cybersecurity program. It is a set of guidelines that helps improve your...
UNDERSTANDING ISO 42001: A GUIDE FOR RESPONSIBLE AI MANAGEMENT SYSTEMS
The invention of artificial intelligence (AI) has changed the operational processes of many industries. However, the rapid growth of technology increases ethical, security, and privacy-related concerns. Therefore, the International Organization for Standardization...