In today’s dynamic and interconnected digital landscape, the efficacy of traditional cybersecurity strategies, such as castle-and-moat defenses, is being increasingly questioned as cyber threats evolve at an alarming pace. Data breaches have become pervasive, impacting not only large enterprises but also small businesses. The reliance on perimeter-based security measures like firewalls and VPNs is proving insufficient against the sophisticated tactics employed by cyber adversaries.
Within this evolving threat landscape, the groundbreaking concept of the Zero Trust security framework emerges as a revolutionary approach. This innovative strategy promotes a continuous verification and least-privilege access model for all users, devices, and applications, irrespective of their whereabouts, representing a departure from traditional cybersecurity practices. The Zero Trust security framework reduces the risks that come from blind trust inside network perimeters by prioritizing thorough inspection and validation at every access attempt. Dive into this blog to explore the key significance and advantages of cybersecurity, specifically zero-trust security.
WHAT IS ZERO TRUST SECURITY?
With its ground-breaking approach to security, the Zero Trust Security model is based on the fundamental tenet that no one should ever be trusted, regardless of whether or not there are people or devices inside the network perimeter. According to this concept, there should be a major move away from implicit trust and toward the deployment of strict authentication and authorization procedures throughout the network architecture. The Zero Trust model subverts the conventional understanding of a trusted perimeter by requiring a thorough examination of each access request. It treats every interaction as possibly coming from an untrusted source until it has been verified through a rigorous process of inspection, authentication, and verification.
Zero Trust Security is based on the strategic idea of “Never trust, always verify,” which is based on the fundamental tenet that implicit trust is a weakness. Fundamentally, Zero Trust works by limiting user access to IT resources by carefully enforcing identity and device verification processes.
This approach’s key components are Zero Trust Identity (ZTI) and Zero Trust Access (ZTA), which guarantee that no person or device, no matter where they are or what kind they are, is automatically granted trust rights. Furthermore, Zero Trust Network Access (ZTNA) enhances security by restricting authenticated users and devices to certain network segments instead of permitting uncontrolled access throughout the whole network.
KEY PRINCIPLES OF ZERO TRUST:
The zero-trust security principles delineate a framework aimed at eradicating inherent trust and enhancing security through the ongoing verification of users and devices.
1. Clarified Verification: Within the framework of Zero Trust Security, explicit verification requires that all access requests, whether coming from inside or outside the organization’s network, go through a rigorous authentication and authorization process. In this way, strict security controls are consistently applied to verify the authenticity of each access attempt and protect against potential threats or unauthorized access.
2. Minimum Access Privilege: The Zero Trust Security paradigm follows the principle of least privilege access, which says that users should only be given the minimal amount of access they need to do their specific tasks. This is done to prevent unauthorized access, lower the risks that come with compromised accounts, and greatly reduce the damage or data breach that could happen in the organization’s network.
3. Constant Monitoring: Constructed within the framework of Zero Trust Security, an all-encompassing surveillance system works diligently to continuously monitor and analyze user behavior as well as device health in real time, making it easier to identify variations and possible breaches early on. This strengthens the organization’s overall security posture and makes it more prepared to react quickly to new threats or suspicious activity observed within the network environment.
4. Precise Segmentation: With a strategic approach, networks are logically divided into smaller, isolated zones with strict access controls, which effectively reduces the possibility of lateral movement within the infrastructure in the event of a breach. At the same time, network resilience is strengthened against a wide range of cyber threats, which promotes a stronger defense posture in protecting organizational resources and confidential data.
5. Data-Centric Security: By utilizing a wide range of effective security measures, careful attention is paid to preserving the integrity of data throughout its entire lifecycle. At this point, advanced encryption methods and strict access controls are used together to make a multi-layered defense system that protects data assets fully not only while they are in storage systems but also while they are being sent across networks and used in the workflows of organizations. This greatly lowers the risk of unauthorized access or potential data breaches and strengthens the organization’s defenses against changing cyber threats and legal compliance obligations.
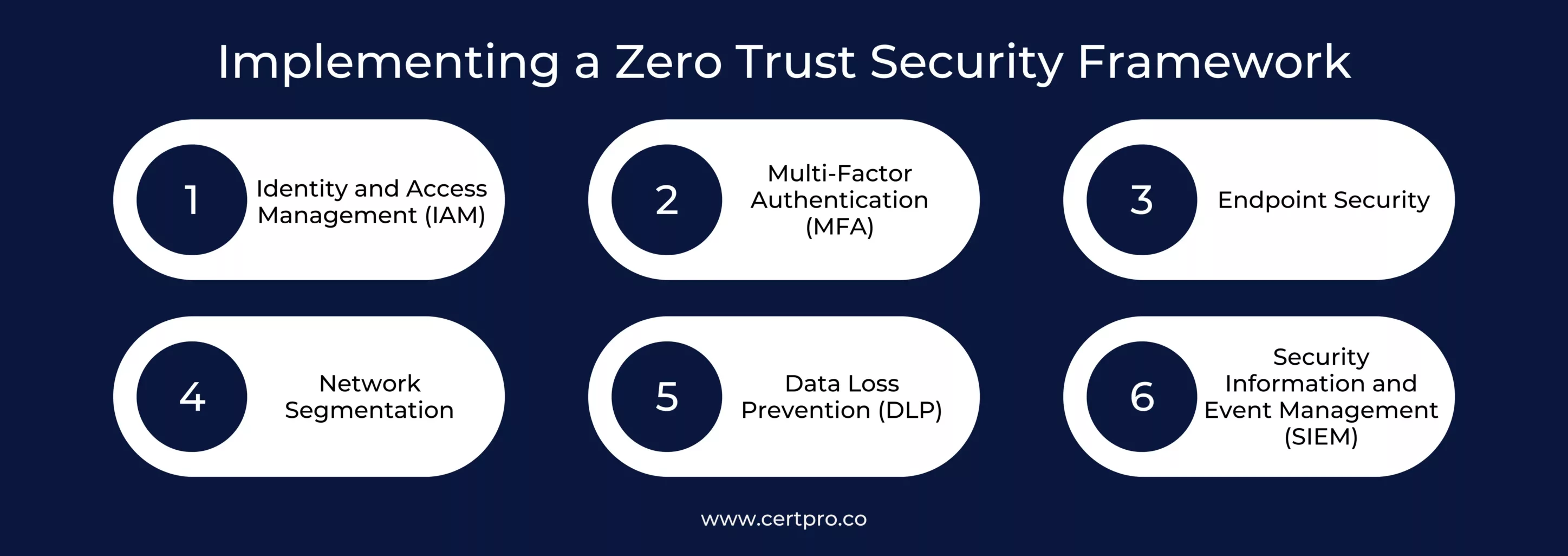
IMPLEMENTING A ZERO TRUST SECURITY FRAMEWORK
A thorough approach that takes into account many security factors is required to implement a Zero Trust security framework. The essential elements of such a framework are as follows:
1. Identity and Access Management (IAM): The process of establishing strong authentication and authorization rules to confirm the identities of people and devices before allowing access to resources is known as identity and access management, or IAM. To guarantee that only authorized organizations are granted access, it is imperative to implement techniques such as biometric verification, certificate-based authentication, and strong passwords.
2. Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA): Enforcing MFA, which requires users to provide many forms of authentication before accessing critical information or systems, will further improve security. To improve authentication procedures, this might involve combining passwords, tokens, biometrics, or even behavioral analysis.
3. Endpoint Security: Endpoint security is critical. This includes safeguarding laptops, cell phones, and Internet of Things devices. To avoid malware infections and illegal access, this entails implementing complete endpoint security solutions that include firewalls, intrusion detection systems, antivirus software, and device encryption.
4. Network Segmentation: Dividing the network into more manageable, separate sections aids in containing and lessening the effects of any intrusions. Organizations can reduce the danger of widespread compromise and restrict the lateral flow of threats by segmenting their network. A few examples of these segmentation criteria include user roles, device kinds, and data sensitivity levels.
5. Data Loss Prevention (DLP): Protecting sensitive data from illegal access, sharing, or exfiltration requires the implementation of data loss prevention (DLP) safeguards. Encryption, access restrictions, and monitoring systems are used in conjunction with data sensitivity classification to guarantee data integrity and confidentiality.
6. Security Information and Event Management (SIEM): Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) systems enable the network-wide collection, analysis, and correlation of security data from various sources. Organizations may enable proactive threat hunting and incident response by centralizing logs and events, which allows for real-time detection and reaction to security problems.
A Zero Trust framework must also include ongoing monitoring, frequent security assessments, and user awareness training in addition to these components. By streamlining security operations and response activities through the integration of automation and orchestration capabilities, the organization’s security posture may also become more resilient overall.
BENEFITS OF ZERO TRUST SECURITY
Making the shift to a Zero Trust security strategy has several benefits, all of which support taking preventative action against growing cyber threats:
1. Elevated Security Posture: The company drastically reduces its attack surface by implementing a continuous verification strategy. This decrease results from the idea that no user or device, no matter where they are in the network, should ever be taken for granted. As a result, such breaches are confined and their effects are reduced, strengthening the security posture as a whole.
2. Improved Threat Identification and Reaction Capabilities: The Zero Trust concept is based on advanced analytics and real-time monitoring, which enable enterprises to quickly identify and address emerging dangers. Security teams may proactively detect malicious actions and promptly address issues before they worsen by closely examining user behavior, network activity, and system abnormalities.
3. Enhanced Adherence to Compliance: The Zero Trust architecture is intrinsically compliant with strict data privacy laws, including the California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA) and the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR). Organizations may guarantee regulatory compliance and preserve sensitive data while avoiding expensive fines by putting strong authentication, access restrictions, and data security mechanisms in place.
4. Improved Agility and Flexibility: By embracing zero trust, employees may work remotely, and the adoption of cloud-based services is facilitated by having secure access to resources from any place. This flexibility supports company continuity and scalability, which in turn stimulate innovation and growth, in addition to meeting the demands of the modern workforce.
5. Decrease in Operational Costs: The Zero Trust model streamlined security measures and increased productivity, resulting in real cost reductions for enterprises. Businesses may maximize resource utilization and reduce overhead costs related to managing complex security environments by automating common operations, doing away with manual procedures, and consolidating security solutions.
Essentially, the Zero Trust method is a proactive response to new threats by providing a comprehensive framework that improves organizational agility, operational efficiency, and regulatory compliance in addition to fortifying defenses.
CYBER SECURITY AND ZERO TRUST
Cybersecurity is crucial as firms shift to hybrid work models amid an increase in cyber threats. This cannot be emphasized enough. Cyber resilience refers to refocusing on realizing the inevitable nature of cyberattacks and ensuring that there are robust processes in place for preparedness, reaction, and recovery. In this framework, Zero Trust appears as a key component for enhancing cyber security.
Nonetheless, a major barrier to the deployment of Zero Trust is the widespread use of fragmented data-centric solutions in most businesses. The hybrid workplace has prompted the implementation of more endpoint solutions, adding to the already complex array of data protection measures. The wide range of technologies available that each apply rules and analytics at various points where sensitive data, people, apps, and devices come together make implementing zero trust challenging. These technologies increase the risk of policy misconfigurations, impede data flow, and reduce visibility.
To successfully reduce the risks of data loss and obfuscation, a strong data security platform should have all-inclusive features such as unified data discovery, categorization, and control procedures. It should also offer an architecture that makes it easier for Zero Trust security to be implemented throughout the organization’s hybrid workplace, enabling security teams to handle complexity with simplicity.
FAQ
Is Zero Trust Security suitable for cloud-based environments?
Yes, Zero Trust Security is applicable to cloud-based environments. In fact, it facilitates secure access to resources from any location, supporting the adoption of cloud services while maintaining stringent security measures.
Can Zero Trust Security be implemented in any organization, regardless of size or industry?
Yes, Zero Trust Security can be tailored to suit the needs of various organizations, irrespective of size or industry. Its principles can be adapted to different infrastructures and security requirements.
How does Zero Trust Security impact user experience and productivity?
While Zero Trust Security may introduce additional authentication steps, it ultimately enhances security without significantly hindering the user experience. By ensuring secure access to resources, it supports productivity and business continuity.
Is Zero Trust Security solely focused on preventing external threats, or does it address insider risks as well?
Zero Trust Security addresses both external threats and insider risks. By continuously verifying users and devices and enforcing least-privilege access, it mitigates the risk of both external breaches and insider threats.
How does the Zero Trust model enhance cybersecurity?
The Zero Trust model enhances cybersecurity by eliminating the assumption of trust within network perimeters. It prioritizes strict verification processes for every access attempt, minimizing the risk of unauthorized access and data breaches.

About the Author
MOHAMMAD YASIN
Mohammad Yasin, Regional Manager in Jordan, is a cybersecurity specialist. With a dedicated focus on securing digital landscapes, he brings extensive experience in compliance and strategic cybersecurity measures to the forefront.
HOW DOES THE NIST CYBERSECURITY FRAMEWORK FUNCTION, AND WHY IS IT IMPORTANT?
Emerging cyber threats make cybersecurity an essential consideration for organizations handling and managing data. In this regard, the NIST cybersecurity framework applies to improving your cybersecurity program. It is a set of guidelines that helps improve your...
UNDERSTANDING ISO 42001: A GUIDE FOR RESPONSIBLE AI MANAGEMENT SYSTEMS
The invention of artificial intelligence (AI) has changed the operational processes of many industries. However, the rapid growth of technology increases ethical, security, and privacy-related concerns. Therefore, the International Organization for Standardization...
EUROPEAN UNION’S ARTIFICIAL INTELLIGENCE ACT: HOW THIS GROUNDBREAKING LAW AFFECTS YOUR BUSINESS
Nowadays, Artificial Intelligence (AI) is transforming our lives exceptionally well. AI is now streamlining healthcare services, providing virtual assistance, and fulfilling queries. Technologies have boons and curses. Similarly, AI creates many concerns about...




