In the age of digital transformation, safeguarding personal data has become a paramount concern. The General Data Protection Regulation and the California Consumer Privacy Act have emerged as pivotal frameworks in the quest for data privacy. Enacted in 2018, GDPR is a sweeping European Union regulation with global reach. The notable distinctions separating CCPA vs GDPR highlight the meaning and differences between CCPA and GDPR.
On the other side of the globe, the law came into effect in 2020 and is specifically aimed at safeguarding the privacy rights of Californian residents. While GDPR casts a broader net in its definition of personal data, the California Consumer Privacy Act emphasizes the consumer’s right to know and control the sale of their personal information.
As we delve into the intricacies of these regulations, this article dissects the salient differences between CCPA and GDPR, shedding light on their contrasting geographic scopes, definitions of personal data, consumer rights, consent mechanisms, and enforcement strategies. Through this exploration, we gain a deeper understanding of how these regulations shape the data privacy landscape and usher in a new era of responsible data management.
WHAT ARE CCPA AND GDPR?
The California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA) and the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) are two significant data privacy regulations designed to protect the rights and personal information of individuals in different regions. Despite originating from distinct jurisdictions—and GDPR vs CCPA from the European Union—both laws share common goals of enhancing privacy and control over personal data.
The CCPA, which became effective on January 1, 2020, focuses on California residents’ data privacy. It grants consumers the right to know what personal information companies collect about them, the ability to opt out of the sale of their data, and the right to request the deletion of their information. The CCPA applies to businesses that exceed certain revenue or data collection thresholds and process Californians’ data.
GDPR, which became enforceable on May 25, 2018, is broader in scope, extending its reach to anyone handling EU citizens’ data, regardless of the organization’s location. Individuals have the right to access personal data, correct inaccuracies, erase data under certain conditions (“right to be forgotten”), and restrict or object to processing. GDPR obliges businesses to obtain explicit consent before collecting personal data and imposes hefty fines for non-compliance.
GDPR and the CCPA comparison regulations emphasize transparency, requiring companies to provide clear privacy policies, secure data storage, and prompt breach notifications. They encourage organizations to implement robust data protection measures, conduct risk assessments, and appoint data protection officers.
The CCPA vs GDPR comparison is vital for addressing data protection concerns by empowering individuals with more control over their personal information. They underscore the growing global importance of safeguarding personal data and promoting ethical data practices among businesses.
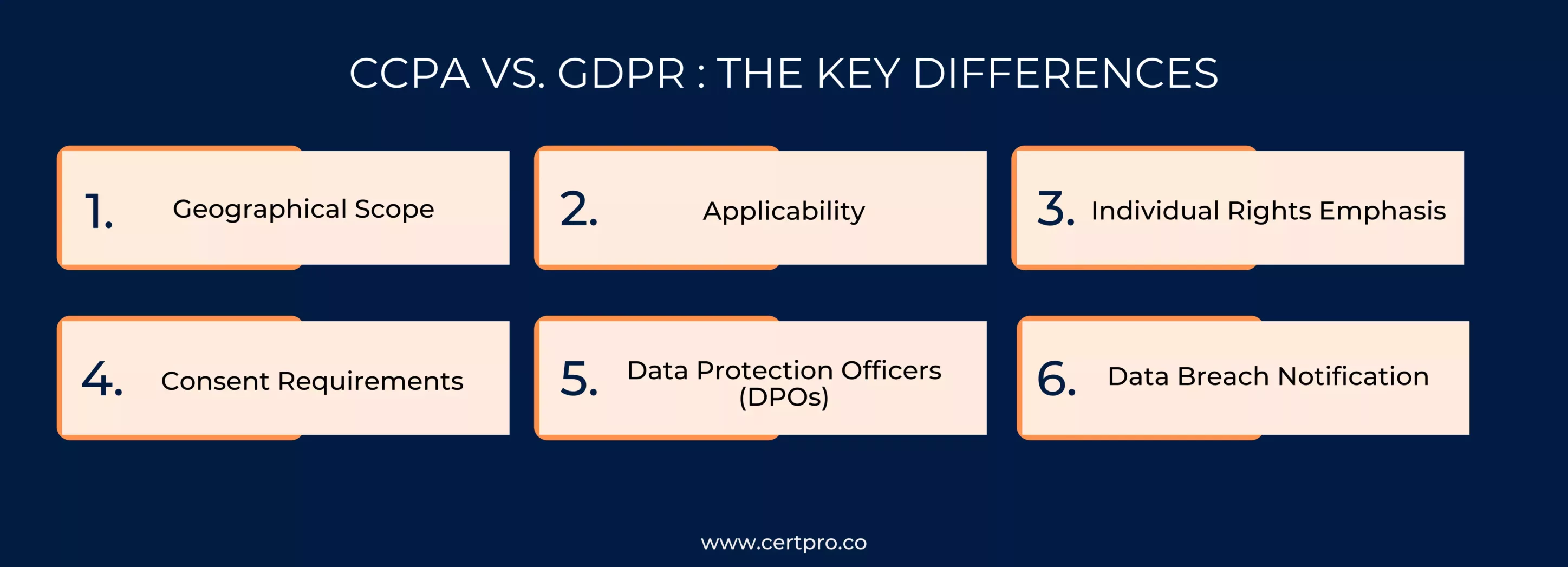
CCPA vs GDPR: THE KEY DIFFERENCES
The California Consumer Privacy Act and the General Data Protection Regulation are two influential data privacy regulations, GDPR vs CCPA, in several significant ways due to their distinct origins, scope, and focus.
1. Geographical Scope:
- CCPA: Primarily applicable to businesses operating in California or dealing with California residents’ data, regardless of the business’s location.
- GDPR: Applies to businesses worldwide that process personal data of EU citizens, extending its reach beyond the EU’s borders.
2. Applicability:
- CCPA: Targets businesses that meet specific revenue or data processing thresholds, focusing on consumer data rights and the sale of personal information.
- GDPR: Encompasses all organizations handling EU citizens’ data, regardless of size or revenue, emphasizing data protection principles and individual rights.
3. Individual Rights Emphasis:
- CCPA: Puts strong emphasis on consumers’ right to opt out of the sale of their data and request its deletion.
- GDPR: Offers a broader range of individual rights, including the right to access data, rectify inaccuracies, restrict processing, and be forgotten.
4. Consent Requirements:
- CCPA: Focuses on the right to opt out of data sales; businesses must provide a “Do Not Sell My Personal Information” option.
- GDPR: Requires explicit and freely given consent for data processing, with strict rules for obtaining and managing consent.
5. Data Protection Officers (DPOs):
- CCPA: It does not explicitly require businesses to appoint a DPO.
- GDPR: Requires certain businesses to appoint a DPO to oversee data protection activities.
6. Data Breach Notification:
- CCPA: Requires businesses to disclose breaches affecting more than 500 California residents to both individuals and the California Attorney General.
- GDPR: Requires breach notification to supervisory authorities within 72 hours if the breach poses a risk to individuals’ rights and freedoms.
In summary, CCPA and GDPR differ in their geographical scope, applicability, individual rights, consent requirements, penalties, and various aspects of their approach to data privacy.
Applicability: CCPA vs GDPR – Who Should Apply?
The GDPR vs CCPA are two important data privacy regulations that aim to protect individuals’ privacy rights in the digital age. They apply to different geographical regions and have some variations in terms of scope and requirements.
1. CCPA (California Consumer Privacy Act): The CCPA is a privacy law that applies to businesses that collect personal information from California residents. It grants California residents certain rights over their personal data, such as the right to know what personal information is being collected, the right to delete their data, and the right to opt out of the sale of their data. The CCPA applies to for-profit businesses that meet certain criteria, including annual gross revenues of over $25 million and the buying, receiving, or sharing of personal information of 50,000 or more California residents. households, devices, or deriving 50% or more of their annual revenues from selling personal information.
2. GDPR (General Data Protection Regulation): The GDPR is a comprehensive data protection regulation that applies to all European Union (EU) member states as well as any organizations outside the EU that process the personal data of EU residents. It establishes strict requirements for how organizations collect, store, process, and transfer personal data. The GDPR applies to both data controllers and data processors. It also grants individuals rights such as the right to access their data, the right to rectify inaccurate data, and the right to be forgotten.
In summary, the GDPR vs.CCPA applies to businesses that collect personal information from California residents, while the GDPR applies to organizations that process the personal data of EU residents, regardless of where the organization is located.
PARTNERING WITH CERTPRO: NAVIGATING DATA PRIVACY
The GDPR and CCPA Comparison reveals both similarities and distinctions. CertPro is taking center stage in the domains of compliance and data protection. Armed with profound expertise in deciphering the complexities of CCPA vs GDPR and other privacy frameworks, CertPro becomes a driving force, enabling businesses to both attain and uphold compliance. Through its innovative solutions, CertPro lends a guiding hand to organizations, aiding in the establishment of resilient privacy protocols, conducting comprehensive risk evaluations, and cultivating an ethos of conscientious data oversight.
In this era of digital transformation, where data is both a currency and a vulnerability, GDPR vs CCPA stand as pillars of protection. As businesses adapt to this new era of data ethics, CertPro stands as a steadfast partner, guiding them towards a future where innovation and privacy coexist harmoniously.
FAQ
WHAT IS THE CALIFORNIA CONSUMER PRIVACY ACT?
The California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA) is a data privacy law that safeguards the personal information of California residents, granting them rights to control data collection and sale by businesses.
WHAT IS THE GENERAL DATA PROTECTION REGULATION REACH?
The General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) has a global scope, extending its influence to organizations across the world that handle personal data belonging to European Union (EU) citizens. This regulation applies regardless of the geographical location of these organizations.
HOW DO THE CALIFORNIA CONSUMER PRIVACY ACT AND GENERAL DATA PROTECTION REGULATION DIFFER?
The California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA) targets Californian residents, focusing on data sale control. The General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) applies globally, emphasizing broader individual rights and strict consent rules for organizations handling EU citizens’ data.
WHO DO THE CALIFORNIA CONSUMER PRIVACY ACT AND GENERAL DATA PROTECTION REGULATION APPLY TO?
CCPA applies to businesses collecting Californian residents’ data, while GDPR applies to global organizations handling personal data of European Union citizens, regardless of their location, emphasizing comprehensive data protection standards and individual rights.
DO THE CALIFORNIA CONSUMER PRIVACY ACT AND GENERAL DATA PROTECTION REGULATION HAVE INDIVIDUAL RIGHTS?
Yes, the CCPA grants California residents rights over data sale, control, and deletion. GDPR provides broader rights, including data access, rectification, erasure, and objection, for European Union citizens’ data handled globally.

About the Author
SHREYAS SHASTHA DRUPADHA
Shreyas Shastha Drupadha, a Senior Business Consultant. Serving as an ISO 27001 Lead Auditor, Shreyas ensures the establishment of robust information security management systems. His expertise also encompasses GDPR, HIPAA, CCPA, and PIPEDA implementation.
HOW DOES THE NIST CYBERSECURITY FRAMEWORK FUNCTION, AND WHY IS IT IMPORTANT?
Emerging cyber threats make cybersecurity an essential consideration for organizations handling and managing data. In this regard, the NIST cybersecurity framework applies to improving your cybersecurity program. It is a set of guidelines that helps improve your...
UNDERSTANDING ISO 42001: A GUIDE FOR RESPONSIBLE AI MANAGEMENT SYSTEMS
The invention of artificial intelligence (AI) has changed the operational processes of many industries. However, the rapid growth of technology increases ethical, security, and privacy-related concerns. Therefore, the International Organization for Standardization...
EUROPEAN UNION’S ARTIFICIAL INTELLIGENCE ACT: HOW THIS GROUNDBREAKING LAW AFFECTS YOUR BUSINESS
Nowadays, Artificial Intelligence (AI) is transforming our lives exceptionally well. AI is now streamlining healthcare services, providing virtual assistance, and fulfilling queries. Technologies have boons and curses. Similarly, AI creates many concerns about...




